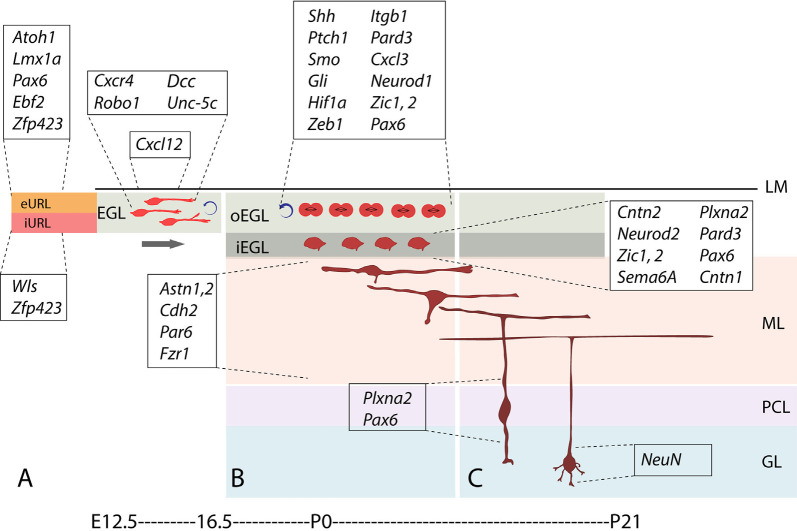
Figure 3.
Stages and stage-specific genes of granule cell development. Schematic representation of some genes playing roles in granule cell birth, proliferation, differentiation, and migration. (A) Atoh1+ granule cell progenitors of the external upper rhombic lip (eURL) derive from ill-defined stem cells of the interior URL (iURL) and migrate to give rise to the EGL thanks to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues (see also Figure 4C), and expand in number between E12.5 and E16.5. (B) After populating the oEGL, GCPs start dividing mostly symmetrically in a process called clonal expansion, promoted by Purkinje cell-secreted sonic hedgehog. Postmitotic GCs form the interior EGL (iEGL) and undertake tangential and radial migration (see text) after extending two axons in the frontal plane (prospective parallel fibers). (C) As they begin their descent into the molecular layer (ML), GC somata extend a radially oriented axon and dendrite, and once in the granular layer, stack with an inside-out progression such that the early-born GCs occupy deeper locations in the GL and project their axons to deeper locations in the ML. Abbreviations: eURL, exterior upper rhombic lip; iURL, interior upper rhombic lip; EGL, external granular layer; oEGL, outer lamina of the EGL; iEGL, inner lamina of the EGL; LM, leptomeninges; ML, molecular layer; PCL, Purkinje cell layer; GL, granular layer.