Figure 9.
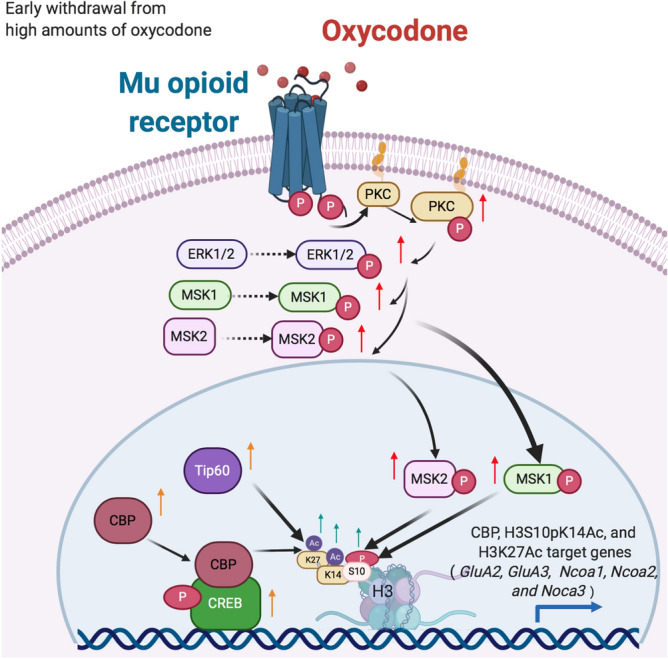
Illustration of the activation of MAPK/MSK signaling pathway in LgA-H rats. Intake of large amount of oxycodone during long-access over 20 days caused increased phosphorylation of PKC, ERK1/2, MSK1, and MSK2. Increased MSK phosphorylation is accompanied by increased histone H3 phosphoacetylation and CREB phosphorylation. In addition, there were increases in the protein expression of two acetyltransferases, CBP and Tip60 that acetylate H3K27. Recruitment of CBP by CREB and histone modifications serve to create a permissible transcriptional environment that led to increased mRNA levels of GluA2 and GluA3 in a MSK1-dependent fashion. This kinase-histone modification cascade may serve as targets for therapeutic interventions against oxycodone use disorder.
