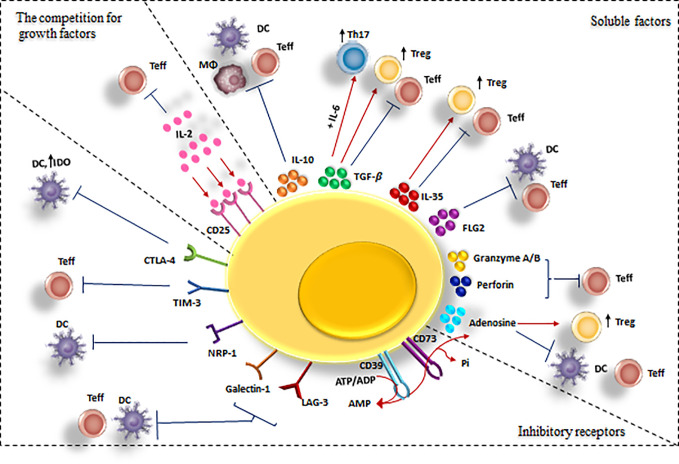
Figure 3.
Cell-mediated suppression mechanisms of Tregs. A variety of molecular mechanisms might operate in a complementary fashion to contribute to Treg-mediated suppression. Tregs exert these suppressive effects on different cell types mainly via three mechanisms: 1) Producing soluble factors such as anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, IL-35, and TGF-β), FLG-2, adenosine, granzyme and perforin. 2) Competing for growth factors: high-affinity CD25 receptors on Tregs and effector T cells compete for the relating ligands.3) Inhibitory receptors: Tregs have been observed to have a direct effect on target cells via interaction of CTLA-4, TIM-3, NRP-1, Gal-1 and LAG-3 and their ligands. CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; DC, dendritic cell; FLG-2, fibrinogen-like protein-2; GAL-1, Galectin-1; LAG3, lymphocyte activation gene 3; TGF, transforming growth factor; Treg , regulatory T cell; Teff, effector T cells; TIM-3, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3; Th17, T helper17; Nrp-1, Neuropilin; MQ, macrophage; IL-2, Interleukin-2; IL-6, Interleukin-6; IL-10, Interleukin-10; IL-35, Interleukin-35.