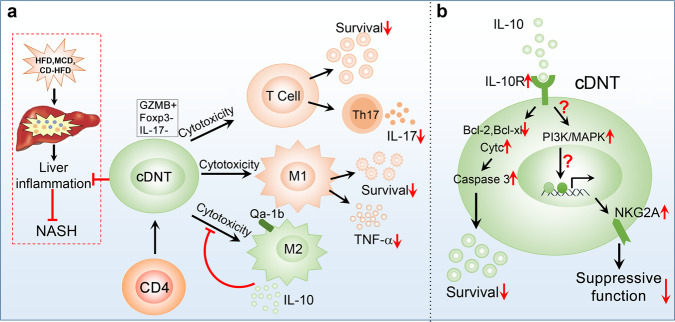
Fig. 8. Mechanisms by which transferred cDNT regulate the liver immune microenvironment and inhibit liver inflammation during NASH development.
a The transferred cDNT not only decreased CD4+ T cell proportion and survival and Th17 cell differentiation, but also selectively suppressed the proportion and cytokine production of liver-infiltrating M1, but not M2 macrophages. IL-10 secreted by M2 macrophages downregulated the immunosuppressive function of cDNT toward M2 macrophages. b The IL-10/IL-10R interaction could decrease Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL expression, and enhance cytochrome C leakage and caspase-3 activity, leading to decreased cDNT survival. The IL-10/IL-10R interaction also activates the PI3K/MAPK signaling pathway, which might induce the expression of the inhibitory receptor NKG2A. The inhibition of cDNT survival and the promotion of NKG2A expression by the IL-10/IL-10R interaction contribute to decreasing cDNT function.