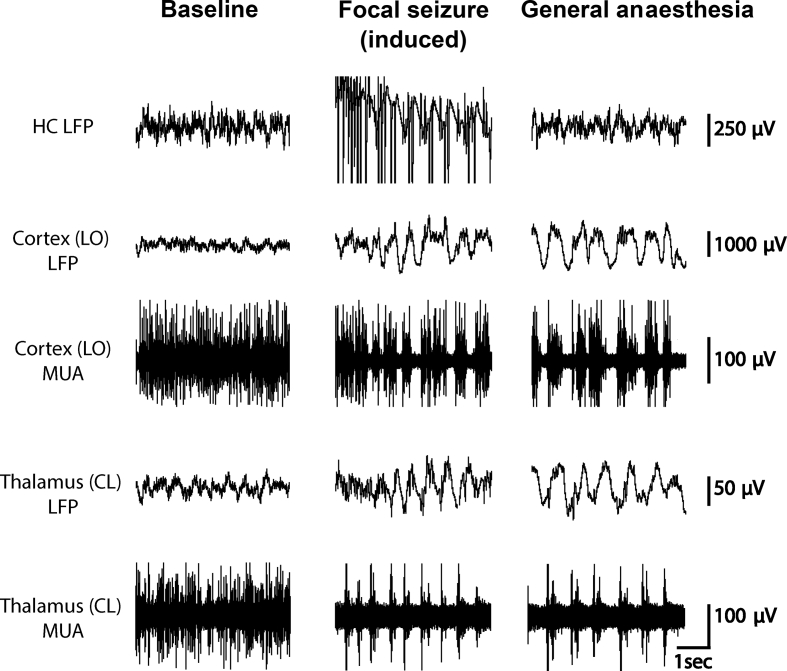
Fig 1.
Comparison of neuronal changes seen in the unconscious states of general anaesthesia and focal onset seizures in a rodent model. Note similar electrophysiologic patterns in the cortex and thalamus in the deeply anaesthetised and seizure states. Data used to produce this figure were obtained by permission from Feng and colleagues.67 Seizures were induced by hippocampal stimulation with a 2 s current injection of 200 micA in the hippocampus with 60 Hz frequency. General anaesthesia was induced with ketamine-xylazine (90/15 mg kg−1) and doses were reduced to establish baseline periods. Local field potential (LFP) filter 0.1–100 Hz. Multi-unit activity (MUA) filter 400 Hz–10 KHz. CL, central lateral nucleus of the thalamus; HC, hippocampus; LO, lateral orbital frontal cortex.