Figure 1.
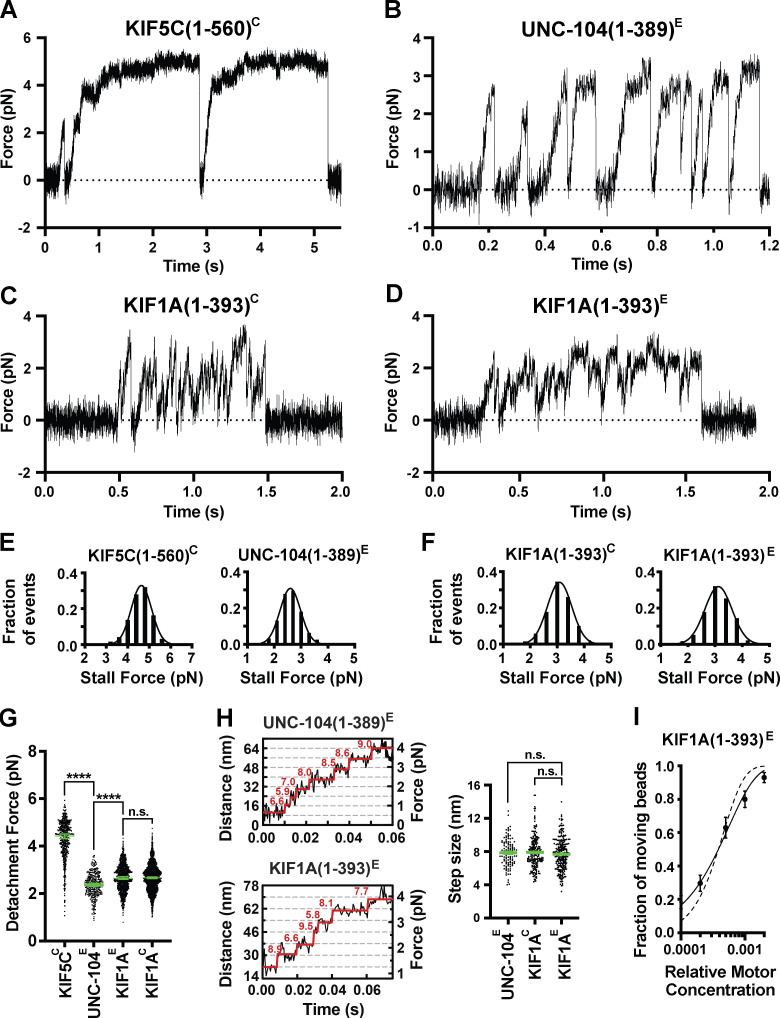
Minimal dimeric KIF1A and UNC-104 motors detach under low force and rapidly reattach to the MT. (A–D) Representative force versus time records of bead movement driven by single molecules of kinesin-1 KIF5C(1–560)C (A), kinesin-3 UNC-104(1–389)E (B), kinesin-3 KIF1A(1–393)C (C), and kinesin-3 KIF1A(1–393)E (D). (E) Stall force histograms of KIF5C(1–560)C (4.64 ± 0.01 pN, mean ± SEM from Gaussian fit; stall plateaus ≥200 ms; n = 197) and UNC-104(1–389)E (2.60 ± 0.01 pN, stall plateaus ≥10 ms; n = 163) compiling forces at k = 0.05–0.06 pN/nm from n = 3 and 2 repeated experiments, respectively. (F) As in E, but for KIF1A(1–393)C (3.09 ± 0.01 pN, n = 418) and KIF1A(1–393)E (3.12 ± 0.02 pN; n = 992) (k = 0.05–0.06 pN/nm; n = 4 and 4). (G) Detachment forces. Green bars indicate the median values with quartiles. KIF5C(1–560)C: 4.43 (3.79, 4.86) pN, n = 557; UNC-104(1–389)E: 2.37 (2.03, 2.70) pN, n = 355; KIF1A(1–393)E: 2.65 (2.25, 3.05) pN, n = 1,044; KIF1A(1–393)C: 2.66 (2.25, 3.01) pN, n = 1,912. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired Welch’s t test (****, P < 0.0001). (H) Left, stepwise forward movements of UNC-104(1–389)E (trap stiffness: k = 0.062 pN/nm; upper inset) and KIF1A(1–393)E (k = 0.057 pN/nm; lower inset). The raw data are shown in black, and the steps detected by the step-finding program are shown in red. Right, measured step sizes. UNC-104(1–389)E: 7.9 ± 0.2 nm, mean ± SEM, n = 109; KIF1A(1–393)E: 7.7 ± 0.1 nm, n = 254; KIF1A(1–393)C: 7.9 ± 0.1 nm, n = 202. Statistical analysis using Welch’s t test shows that the step-size distributions are statistically indistinguishable. (I) Fraction of KIF1A(1–393)E-coated beads binding to and moving along MTs as a function of the relative motor concentration. The bead concentration was kept constant for all measurements, whereas the motor concentration was varied (n = 224 total number of beads tested; n = 70–100 at each concentration). The solid line represents the fit to the Poisson distribution 1 − exp(−λC) for one or more motor molecules (processive model), where C is the relative motor concentration and λ is a fit parameter (R2 = 0.9886; Svoboda and Block, 1994). The dotted line represents the fit to the distribution 1 − exp(−λC) − (λC)exp(−λC) for two or more molecules (nonprocessive model; R2 = 0.9023). Data values are displayed as the mean ± square root of [f(1 − f)/n], with n being the number of beads tested. n.s., not significant.