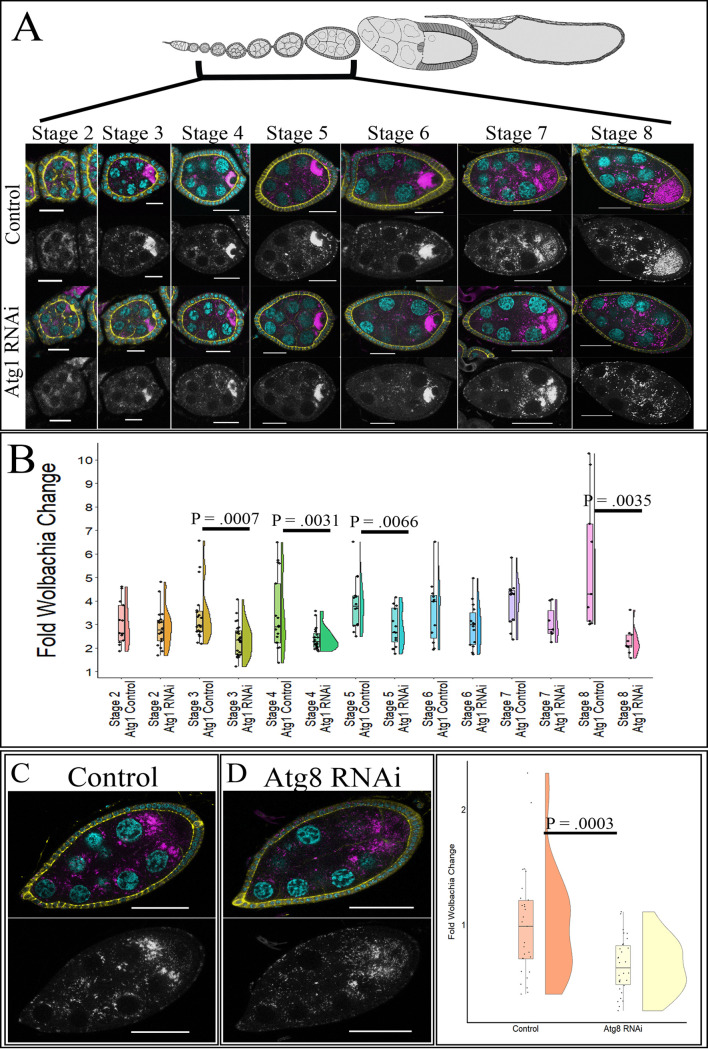
FIG 5.
Knockdown of autophagy in the female germ line decreases wMelCS density. Stage-specific confocal analysis reveals a decrease in relative Wolbachia density upon knockdown of autophagy genes during multiple stages of development. NGT;nos was used to knockdown Atg1, and MTD was used to knockdown Atg8a. DNA is colored cyan, D cadherin (labeling the follicle cells) is yellow, and a fluorescently labeled DNA probe detecting Wolbachia is in magenta. Grayscale images display the Wolbachia-only channel. (A) Representative confocal z-stack images of control and Atg1 knockdown in the germ line of wMelCS-infected flies. (B) Quantification of wMelCS-infected stage-specific egg chambers upon Atg1 knockdown. Statistically significant P values are reported only. (C) Representative confocal z-stack images of wMelCS-infected stage-8 egg chambers for control flies display a high Wolbachia density. (D) Representative confocal z-stack images of wMelCS-infected stage-8 egg chambers with Atg8 RNAi expressed display reduced germ line Wolbachia density. (E) Quantification of wMelCS-infected stage-8 egg chambers for the control and Atg8 knockdown reveal decreased density upon germ line expression of Atg8 RNAi. Scale bars, 10 µM for stages 2 and 3, 20 µM for stages 4 to 6, and 40 µM for stages 7 and 8. Student’s t tests were conducted to determine significance.