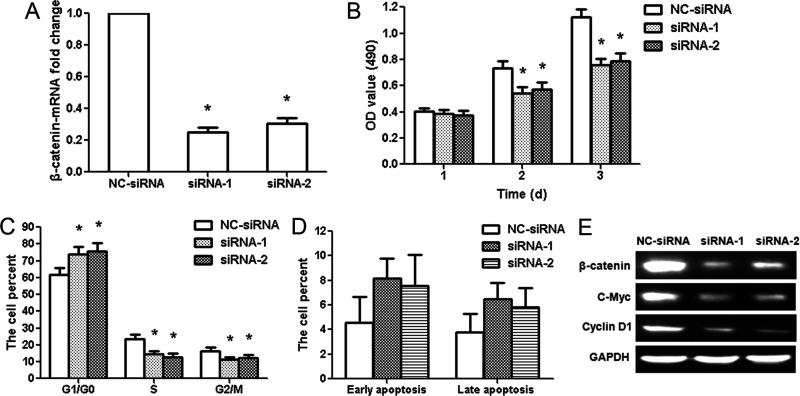
Figure 5.
β-Catenin small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) inhibit the proliferation of glioma LN229 cells. (A) qRT-PCR results showed the knockdown efficiency of β-catenin siRNAs in LN229 cells. (B) MTT assay showed that β-catenin siRNAs decreased the activity of LN229 cells at 2 and 3 days. (C) Flow cytometry analysis showed the percentage of cells in the G1/G0, S, and G2/M phases. G1/G0 phase cells increased after β-catenin siRNA treatment, whereas S and G2/M phase cells decreased. (D) The data showed the percentage of early and late apoptosis after β-catenin siRNA treatment. (E) β-Catenin, c-Myc, and cyclin D1 protein expressions were examined after β-catenin siRNA treatment. *p < 0.01, compared with the NC-siRNA group, n = 3.