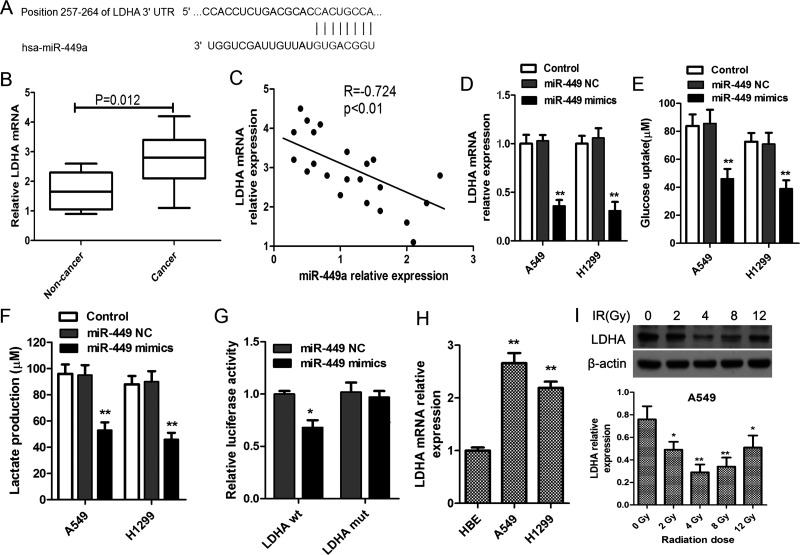
Figure 4.
miR-449a targets lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) to suppress its expression. (A) LDHA mRNA levels in NSCLC tissue samples and matched noncancerous normal tissue samples (n = 22). (B) Bioinformatic prediction of the binding site of miR-449a on the 3′-untranslated regions (3′-UTRs) of LDHA. (C) Correlations of miR-449a and LDHA mRNA levels in NSCLC tissues. (D) A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with miR-449a mimics or negative control oligonucleotide, and miR-449a levels were evaluated using qRT-PCR after 24 h. Glucose uptake (E) and lactate production (F) in lung cancer cells in response to miR-449a upregulation by miR-449a mimics. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, versus control. (G) Luciferase assay of the binding of miR-449a on LDHA. A549 cells were cotransfected with miR-449a mimics, NC oligonucleotide, and a luciferase reporter containing LDHA 3′-UTR (LDHA wt) or mutant constructs of LDHA (LDHA mut). Then relative luciferase activity was determined. *p < 0.01, versus miR-449 NC. (H) LDHA mRNA levels in normal lung cell HBE and lung cancer cells (A549 and H1299). **p < 0.01, versus HBE. (I) A549 cells were exposed to escalating doses of radiation ranging from 2 to 12 Gy, and the expression of LDHA was detected using Western blot after incubation for 24 h. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, compared to 0 Gy. All experiments were repeated at least in triplicate.