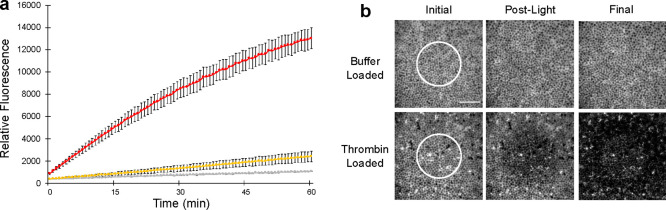
Figure 4.
a. Thrombin catalytic activity was assessed using commercially available fluorescent thrombin benzoyl-FVR-(aminomethylcoumarin). Illumination of RBCs internally loaded with thrombin and surface modified with C18-Mel/C18-Cbl-BS (red curve). Unilluminated RBCs internally loaded with thrombin and surface modified with C18-Mel/C18-Cbl-BS (yellow curve). Illumination of thrombin-loaded control lacking the surface modified photolytic trigger (gray curve). Error bars represent standard deviation. b. RBCs surface modified with C18-Mel/C18-Cbl-BS were incubated with (Alexa Fluor 647)-fibrinogen and imaged using a confocal microscope. The region of photolysis (photolytic dwell time 10 μs/pixel, 80% power of 515 nm laser) is highlighted prior to (left), immediately after (middle), and 210 s after (right) 515 nm exposure. Surface modified RBCs that were internally buffer-loaded (top row) do not induce conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. By contrast, thrombin-loaded RBCs that contain the surface phototrigger (bottom row) provoke the formation of an insoluble fibrin gel matrix immediately after photolysis. The fibrin matrix rapidly spreads throughout the field of view within 3.5 min. Scale bar represents 50 μm.