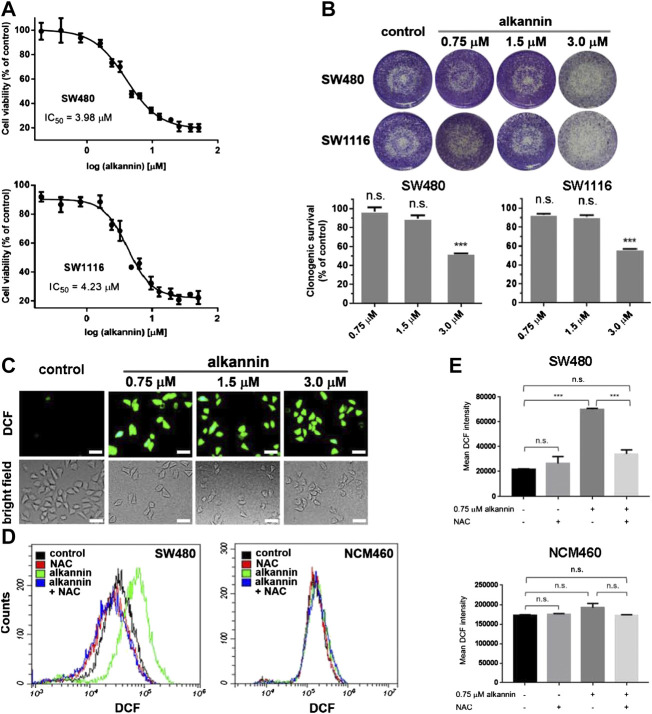
FIGURE 1.
Sublethal doses of alkannin elevate ROS levels in colorectal cancer cells. (A) MTT assay. Cells were treated with 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 2.4, 3.2, 4.8, 6.4, 9.6, 12.8, 19.2, 25.6, 38.4 or 51.2 μM alkannin for 24 h. The IC50 values of alkannin against the SW480 and SW1116 colorectal cancer cell lines were calculated using the GraphPad Prism software. Data were shown as average ± SD from three independent experiments. (B) Colony formation assay. SW480 and SW1116 cancer cells were treated with alkannin at the indicated doses for 7 days and data from three independent experiments were presented as mean ± SD. (C) Representative images of DCFH-DA staining. SW480 cells were treated by alkannin at the indicated doses for 3 h (scale bars: 50 μm). (D) Measurement of ROS by flow cytometry. Treatment by 0.75 μM alkannin for 3 h induced a significant ROS increase in the SW480 cancer but not the NCM460 noncancerous cells. NAC suppressed the ROS increase in the cancer cells. (E) Quantification of flow cytometry measurements of ROS (n = 3). n.s.: not significant, *:p < 0.05, ***:p < 0.001.