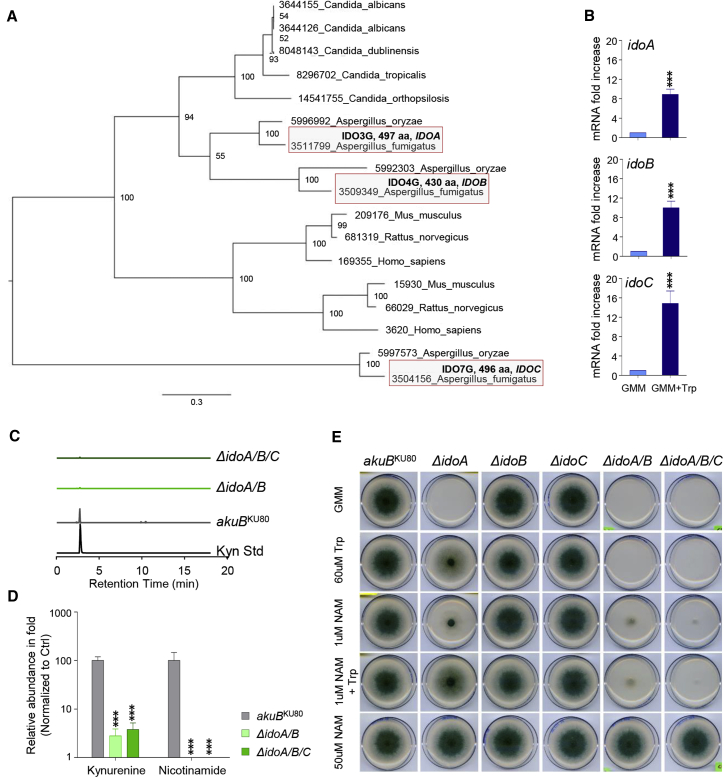
Figure 1.
Aspergillus Idos catabolize Trp for NAD+ and kynurenines biosynthesis
(A) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis of IDOs.
(B) mRNA fold increase of Aspergillus idoA, idoB, and idoC in GMM and GMM + Trp at 24 h of culture.
(C and D) Peak levels and relative abundance of l-kynurenine (Kyn) and nicotinamide (D) in WT (Aspergillus akuBKU80) and mutant strains inoculated on solid GMM supplemented with NAM and Trp and cultured at 37°C for 84 h in triplicates.
(E) Growth of parental akuBKU80and mutant strains in GMM, GMM + Trp (60 μM), and NAD supplementation (NAM) to the growth medium.
(B and D) Data are represented as mean ± SD. Graphs are representative of data collected from three independent replicate experiments.
(B) Statistical significance (∗∗∗p < 0.0001) was determined against the untreated (GMM) (two-tailed Student’s t test unpaired parametric).
(D) Statistical significance (∗∗∗p < 0.0001) was determined against the Aspergillus akuBKU80 strain (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s akuBKU80 versus ΔidoA/B and versus ΔidoA/B/C).
(C and E) Experiments were repeated three times.
See also Figures S1–S4.