Figure 2.
Aspergillus Trp alternative metabolism: the Aro pathway
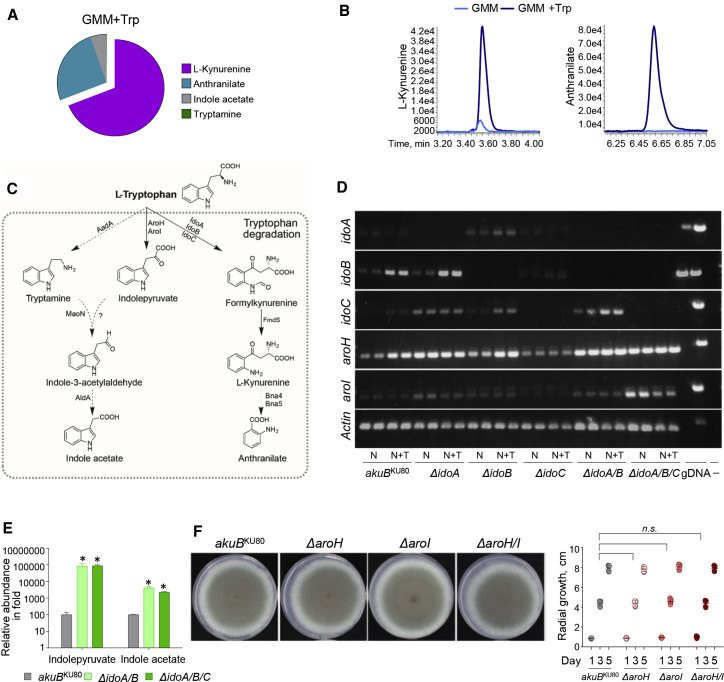
(A and B) Pie diagram and peak levels of Trp-derived metabolites performed at 24 h of culture in GMM + Trp by targeted metabolomics of Aspergillus WT strain.
(C) Trp metabolic pathways, enzymes, and molecular structures of Trp-indole derivatives.
(D and E) RT-PCR of Aspergillus genes involved in the catabolic pathway (D) and relative abundance of indole-derivatives in WT (Aspergillus akuBKU80) and mutant strains inoculated on solid GMM supplement with NAM and Trp and cultured at 37°C for 84 h (E).
(F) Radial growth of Aspergillus akuBKU80 and A. fumigatus aro mutants. Strains were inoculated with 104 conidia onto the solidified GMM supplemented with 5 mM l-Trp. Colony diameters of each strain were measured after 1, 3, and 5 days of growth at 37°C.
(A, B, and D) Experiments were repeated three times. Statistical significance (∗∗p < 0.001) was determined against the Aspergillus akuBKU80 strain (unpaired t test: akuBKU80 versus ΔidoA/B and versus ΔidoA/B/C).
See also Figures S4 and S5.