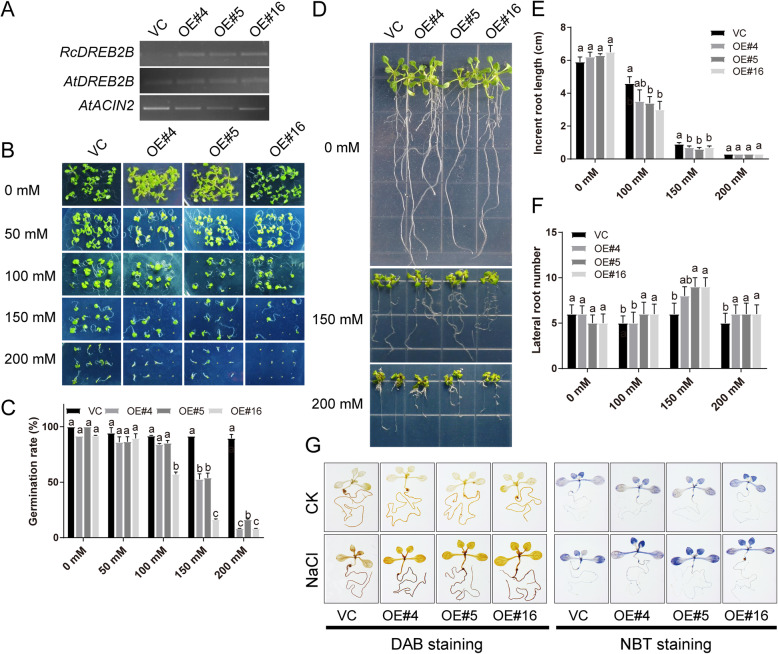
Fig. 6.
Seed germination and post-germination assays of VC and RcDREB2B overexpressed lines in response to NaCl. a RT-PCR analysis of RcDREB2B and AtDREB2B in the overexpressed lines. The specific primers of RcDREB2B were used to test transgene levels. AtACTIN2 was used as an internal control. Uncropped gel images are provided in Additional file 7: Figure S5. b Seed germination performance of RcDREB2B overexpressed lines (OE#4, 5, 16) and VC on MS supplement with various NaCl concentrations (0, 50, 100, 150, and 200 mM). c Germination rates of seeds indicated in (b). Seed germination was monitored with radicle emergence and cotyledon greening after 9 d of post-stratification. Twenty seeds from VC and RcDREB2B transgenic lines were used with three biological replicates and means of + SE. Different letters stand for P < 0.5, using one-way ANOVA analysis. d Root growth performance of RcDREB2B overexpressed lines (OE#4, 5, 16) and VC in response to NaCl. 6 d old seedlings of VC and RcDREB2B transgenic plants were placed on MS plates supplemented without and with 150 or 200 mM NaCl for 10 days, respectively. Comparisons of increment in root length (e) and lateral root numbers (f) of VC and RcDREB2B overexpressed lines. Data indicate means + SE of three biological replicates. Different letters indicate P < 0.5, using one-way ANOVA analysis. g Histochemical staining assay detecting O2− and H2O2 accumulation with nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) and 3,3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) in VC and RcDREB2B transgenic seedlings under normal growth or salt stress. We present results as means ± SD. n = 3