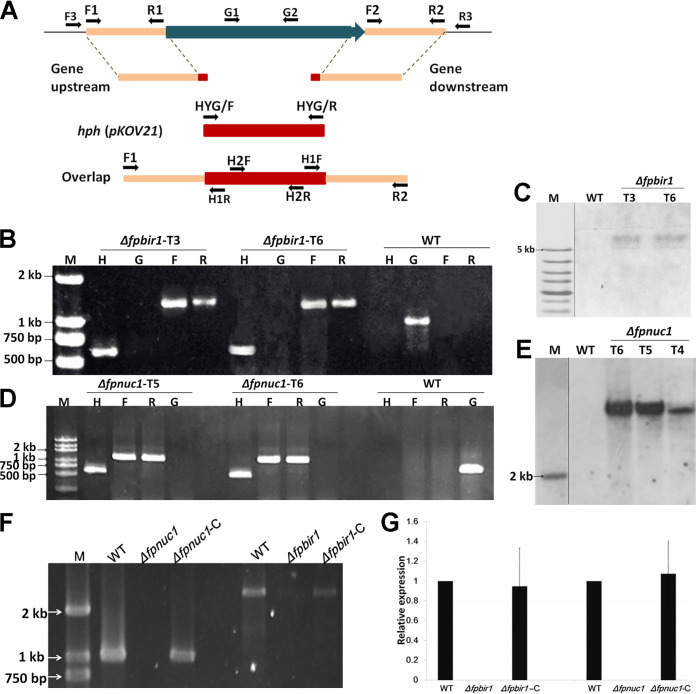
FIG 3.
Construction of FpBIR1 and FpNUC1 deletion mutants. (A) Schematic representation of the genome regions of target genes and primer locations used for gene replacement using the split-marker strategy and mutant. (B and D) Verification of incorporation into genomic DNA by PCR using four primer pairs, which were used to analyze hph (H2F and H2R), upstream (F3 and H1R), downstream (H1F and R3), and target gene (G1 and G2) presence. Amplified fragments for FpBIR1 replacement were 610 bp, 1,328 bp, 1,363 bp, and 638 bp. Amplified fragments for FpNUC1 replacement were 610 bp, 1,292 bp, 1,348 bp, and 737 bp. WT, wild-type strain WZ 2-8A; M, molecular markers; H, hph gene; G, target gene; F, upstream; R, downstream. (C and E) Southern blot analysis using digoxigenin-labeled hph gene and XhoI-digested FpBIR1 deletion mutant genomic DNA and BamHI-digested FpNUC1 deletion mutant genomic DNA. (F) PCR products for the gene complementation constructs. A 2,625-bp fragment was amplified from the FpBIR1 complementation strain, and a 1,041-bp fragment of FpNUC1 was amplified from the FpNUC1 complementation strain. (G) Expression levels of target genes assessed by qRT-PCR. Bars represent standard deviations from three independent RNA isolations and qRT-PCR replicates.