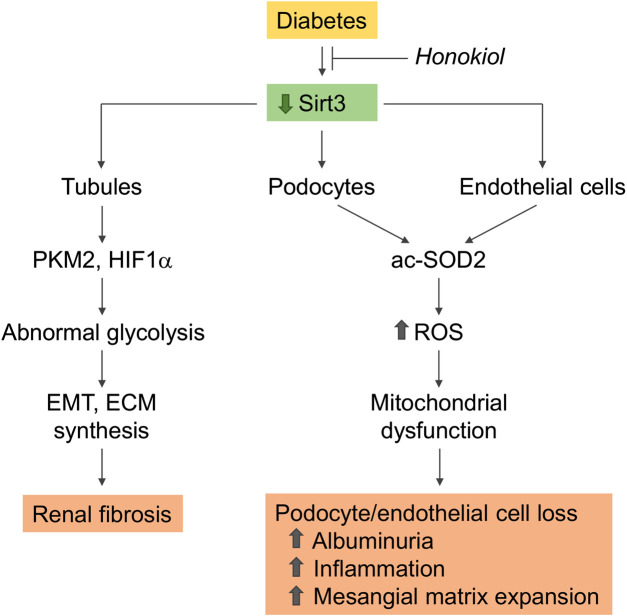
FIGURE 2.
Role of sirtuin-3 dysregulation in kidney disease progression in diabetes. Sirtuin-3 is downregulated in the diabetic kidney. Reduced expression in podocytes and glomerular endothelial cells impairs SOD2 antioxidant activity as a consequence of enzyme acetylation, resulting in increased ROS generation, which promotes mitochondrial dysfunction and cell loss. These changes contribute to the development of albuminuria associated with inflammation and mesangial matrix expansion. Renal tubules with reduced sirtuin-3 undergo a metabolic reprogramming with a shift toward abnormal glycolysis, display EMT, and acquire a profibrotic phenotype. Rescuing sirtuin-3 by the specific activator honokiol prevents glomerular and tubule dysfunction and ameliorates diabetic nephropathy. acSOD2, acetylated SOD2; PKM2, pyruvate kinase isozyme M2; EMT, epithelial to mesenchymal transition; ECM, extracellular matrix.