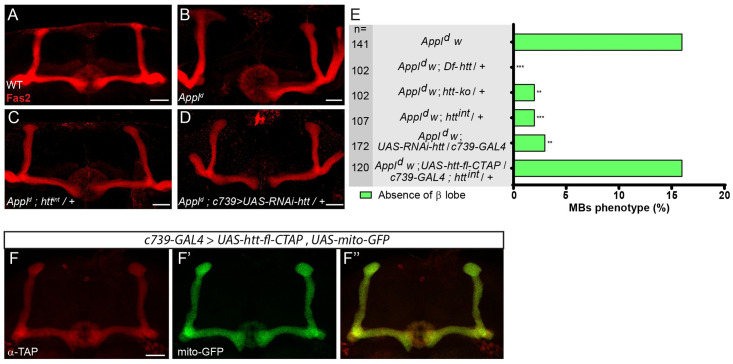
Fig 1. The loss of htt rescues the Appld MB axon outgrowth mutant phenotype.
(A) Wild-type MB α and β lobes revealed by anti-Fas2 staining. (B-D) Anti-Fas2 staining reveals the absence of the β lobe in an Appld mutant brain (B), which is rescued by the loss of one copy of htt (C) and is also rescued by the expression of RNAi against htt driven by c739-GAL4 (D). (E) Quantitation of rescue of the MB Appld phenotype by Df-htt, htt-ko, httint and UAS-RNAi-htt driven by c739-GAL4. The rescue of Appld by httint is prevented by the overexpression of htt driven by c739-GAL4 indicating the functionality of the UAS-htt-fl-CTAP transgene. n = number of MBs analyzed, ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001. Significance was calculated by a multiple comparison Fisher’s exact test (P = 5.8 10−10) followed by post-hoc Bonferroni’s multiple comparison correction (p-values = 2.3 10−5, 0.0018, 0.0009, 0.0014 and 1). (F-F”) The expression of UAS-htt-fl-CTAP revealed by an anti-TAP staining (F) and UAS-mito-GFP (F’) driven by c739-GAL4 are similar in the MBs (F”). All panels correspond to adult brains. The scale bar on panels A-D and F indicates 30 μm. Images are composite stacks to allow the visualization of axon trajectories along their entire length. Full genotypes: (A) y w67c23 / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / +. (B) Appld w*/ Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / +. (C) Appld w* / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP /+; httint / +. (D) Appld w* / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / UAS-RNAi-htt. (E) top to bottom: Appld w* / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / +. Appld w* / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / +; Df-htt / +. Appld w* / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / +; htt-ko / +. Appld w* / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / +; httint / +. Appld w* / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / UAS-RNAi-htt. Appld w* / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / UAS-htt-fl-CTAP; httint / +. (F-F”) y w67c23 / Y; c739-GAL4 UAS-mito-GFP / UAS-htt-fl-CTAP.