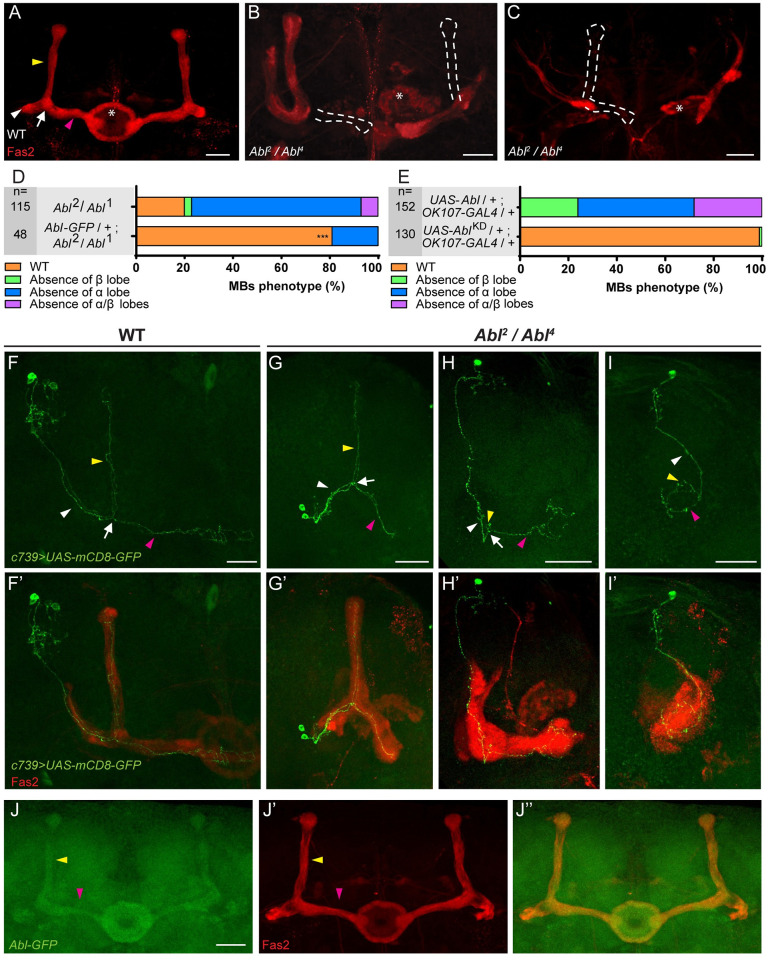
Fig 3. Either loss or overexpression of Abl affect MB αβ neuron morphology.
(A-C) Anti-Fas2 staining on wild-type (WT) brain (A) and on Abl2/Abl4 brain (B-C). In a wild-type (WT) brain, the α lobe (indicated by yellow arrowhead) projects vertically and the β lobe, indicated by pink arrowhead, projects toward the midline and stops before reaching it. The loss of the β and α lobes (B) and of both the α and β lobes (C) is emphasized by white dashed lines. * shows the ellipsoid body. (D) Quantitation of the αβ neuron mutant phenotype in the Abl2/Abl1 mutant and rescued brains with the Abl-GFP genomic transgene. n = number of MB observed and *** P < 0.001 (Fisher exact test). Transgenic expression of Abl-GFP rescued the morphological defect and lethality of the double heterozygous Abl2/Abl1 combination, but failed to rescue Abl2 homozygote lethality, indicating that this lethality is due to associated modifiers on the chromosome independent of Abl. (E) Quantitation of the αβ neuron mutant phenotype when a wild-type or a kinase dead form of Abl expression is driven in the MBs by OK107-GAL4 (n = number of MB observed). (F-F’) Two-cell WT αβ neuron MARCM clone in a WT brain (F) associated with anti-Fas2 staining in red (F’). (G-G’) Two-cell WT-looking αβ neuron clone (G) associated with anti- Fas2 staining in red (G’) in an Abl2/Abl4 brain. (H-H’) A single-cell αβ neuron clone with an α branch growth defect (H) associated with anti-Fas2 staining in red (H’) in an Abl2/Abl4 brain displaying an absence of α lobe. Note the α branch which stops just after the branching point in H (yellow arrowhead). (I-I’) A single-cell αβ neuron clone with α and β branch growth defects (I) associated with anti-Fas2 staining in red (I’) in an Abl2/Abl4 brain displaying an absence of α and β lobes. Note the small α and β branches in I. (J-J”) Expression of Abl within the MB using an Abl-GFP genomic transgene (J). α and β lobes are revealed by anti-Fas2 staining in red (J’). Merge of GFP and anti-Fas2 staining (J”). All panels correspond to 48 hAPF brains except for E and the rescue experiment in D which are from adult brains. White arrowheads show the peduncle or common part of the αβ axon, white arrows show the αβ branch point, yellow arrowheads show the α axon branch or the α lobe and pink arrowheads show the β axon branch or the β lobe. The scale bar in panels A-C and F-J indicates 30 μm. Images are composite stacks to allow the visualization of axon trajectories along their entire length. Full genotypes: (A) wild type: y w67c23. (B and C) y w67c23;; Abl2 FRT2A / Abl4 FRT2A. (D) top to bottom: y w67c23;; Abl2 FRT2A / Abl1 FRT2A. y w67c23; Abl-GFP / +; Abl2 FRT2A / Abl1 FRT2A. (E) top to bottom: y w67c23 / Y; UAS-Abl / UAS-mCD8-GFP;; OK107-GAL4 / +. y w67c23 / Y; UAS-AblKD / UAS-mCD8-GFP; TM6B,Tb1 / +; OK107-GAL4 / +. (F) w* tubP-GAL80 hs-FLP122 FRT19A / w* sn FRT19A; c739-GAL4 UAS-mCD8-GFP / UAS-mCD8-GFP. (G-H-I) w* tubP-GAL80 hs-FLP122 FRT19A / w* sn FRT19A; c739-GAL4 UAS-mCD8-GFP / UAS-mCD8-GFP; Abl2 / Abl4. (J) y w67c23; Abl-GFP / +.