Fig 3. Cellular differentiation is associated with clonal expansion of HIV proviruses.
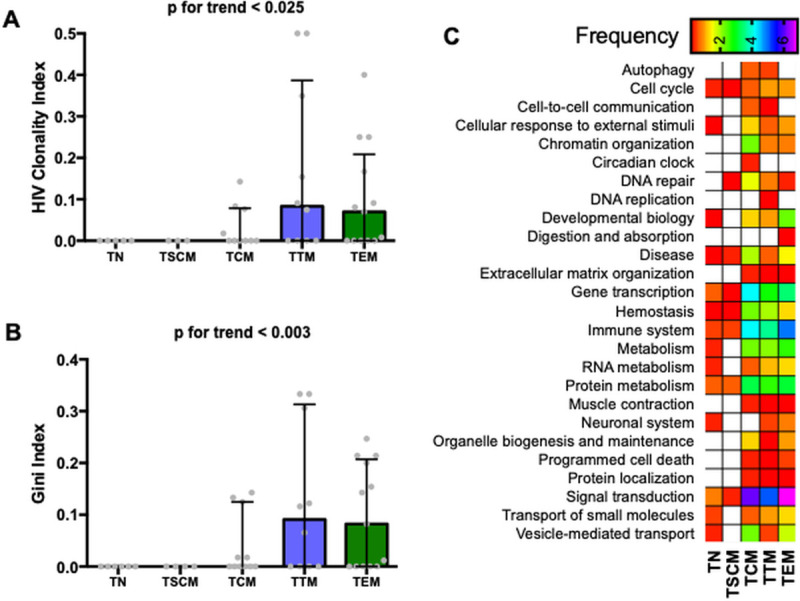
HIV integration site analysis was performed on the following resting CD4 T cell subpopulations: naïve (TN), stem-cell memory (TSCM), central memory (TCM), transitional memory (TTM) and effector memory (TEM) cells. Medians and interquartile ranges are presented and only significant p values are shown. A. The HIV clonality index is calculated as the proportion of integration sites that are clonally expanded over the total number of integration sites detected. B. The Gini index is a measure of statistical dispersion intended to represent the integrated events distribution of an integration position, with values ranging from 0–1 from perfectly even (uniform clones) to highly skewed and uneven (many small clones and a few vastly expanded clones). C. Proportion of total unique HIV integration sites detected across all CD4 T cell subpopulations that fall within a given reactome (a set of linked genes, defined by an open source database of biologic pathways) and CD4 subpopulation. Specifically, the numbers reflect the total number of unique integration sites within a given reactome and CD4 subpopulation divided by the total number of integration sites detected across all CD4 subpopulations, multiplied by 100. Low frequencies are depicted in red while high frequencies are in purple.
