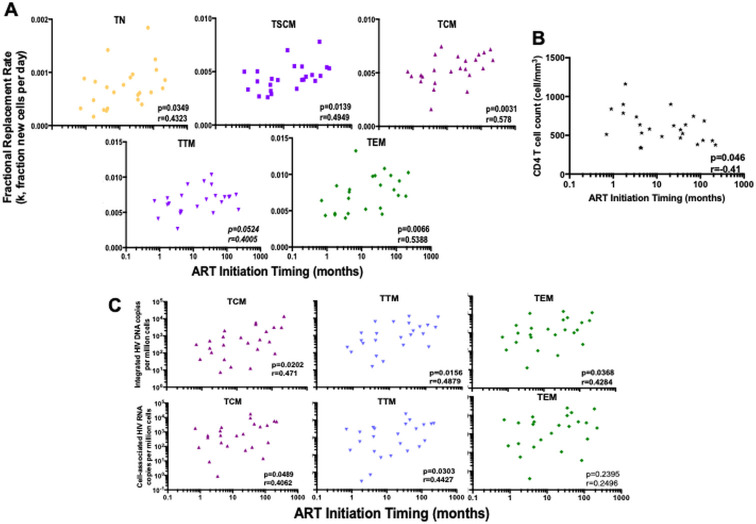
Fig 4. Early ART is associated with lower fractional replacement rate and HIV burden in resting CD4 T cell subpopulations.
Measurements of the fractional cell replacement rate and HIV genome levels were performed in resting CD4 T cell subpopulations: naïve (TN), stem-cell memory (TSCM), central memory (TCM), transitional memory (TTM) and effector memory (TEM) cells. Each symbol represents a participant’s sample and the data are plotted on a log10-scale axis. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation time is expressed in months. Spearman correlation coefficients (ρ) and associated p-values are reported in each subplot. A. The relationship between the fractional replacement rate and the initiation time of ART was assessed. The fractional replacement rate (k) is estimated as cells produced per day. B. The relationship between peripheral CD4 T cell count and the initiation time of ART was assessed. CD4 T cell count is estimated as cells per mm3 of blood. C. The associations between HIV nucleic acid levels and ART initiation time are shown for all participants. Integrated HIV DNA and cell-associated HIV RNA are measured and presented as copy number per million cells. Cell subpopulations that contribute most of the HIV reservoir are shown here, i.e., TCM, TTM and TEM. Undetectable values were assigned a value equal to the threshold of detection based on the number of cells analyzed.