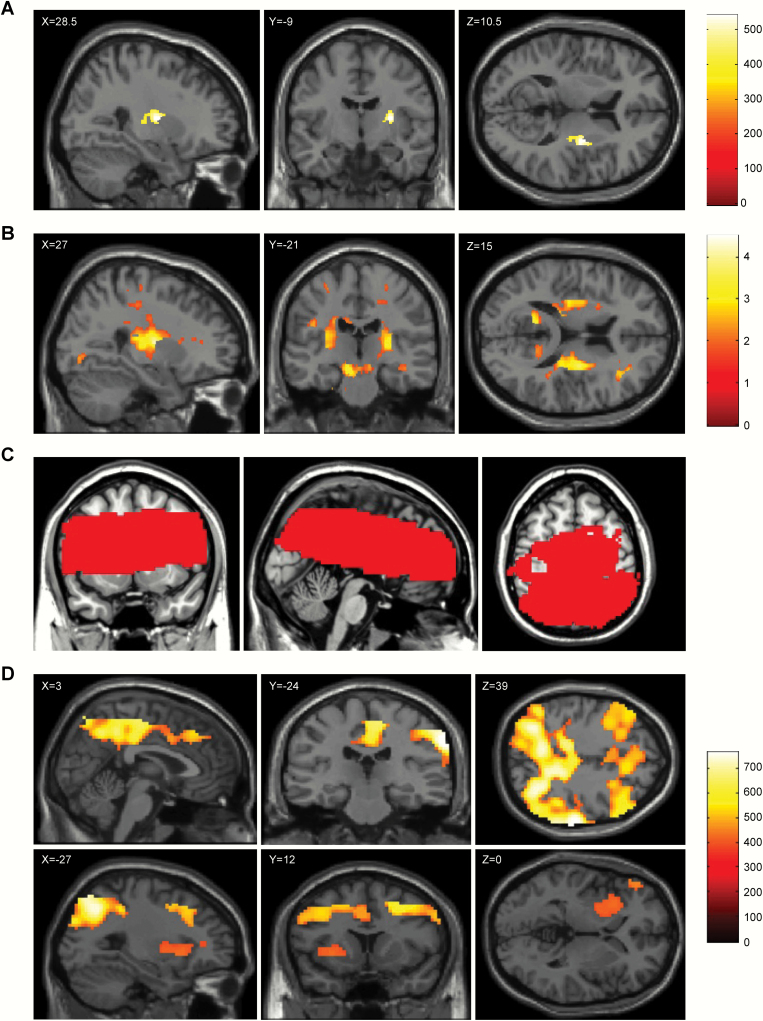
Fig. 2.
Brain regions showing significant associations of the OLIG2 gene polymorphism rs1059004 with fractional anisotropy and regional cerebral blood flow. (a) The white matter region where the positive association between the fractional anisotropy and number of A alleles of the OLIG2 gene polymorphism rs1059004 was observed based on threshold-free cluster enhancement, with the significance level set at P < .05 (corrected for familywise error rate based on 5000 permutations), is shown in yellow-orange. The associated region is overlaid on a single-subject T1 SPM8 image. Significantly associated white matter was widespread in the right posterior limb of the internal capsule, the right retrolenticular part of the internal capsule, and the right external capsule. The anatomical labels and significant clusters of major white matter fibers were determined using the ICBM DTI-81 Atlas (http://www.bmap.ucla.edu/portfolio/atlases/ICBM_DTI-81_Atlas/).28 (b) The white matter region where the positive association between the fractional anisotropy and the number of A alleles of the OLIG2 SNP rs1059004 was observed, with the significance level set at P < .05 (uncorrected for multiple comparisons), is shown in yellow-orange. The associated region was overlaid on a single-subject T1 SPM8 image. Significantly associated white matter was widespread in the bilateral posterior limb of the internal capsule, the bilateral retrolenticular part of the internal capsule, and the bilateral external capsule. (c) Brain regions marked in red indicate the target areas of the brain analyzed with arterial spin labeling analyses. (d) The brain region where the positive association between the mean resting cerebral blood flow and the number of A alleles of the OLIG2 gene polymorphism rs1059004 was observed based on threshold-free cluster enhancement, with the significance level set at P < .05 (corrected for familywise error rate based on 5000 permutations), is shown in yellow-orange. The associated region is overlaid on a single-subject T1 SPM8 image. Significantly associated brain regions included the precuneus, middle and posterior cingulate cortices, putamen, insula, and globus pallidus.