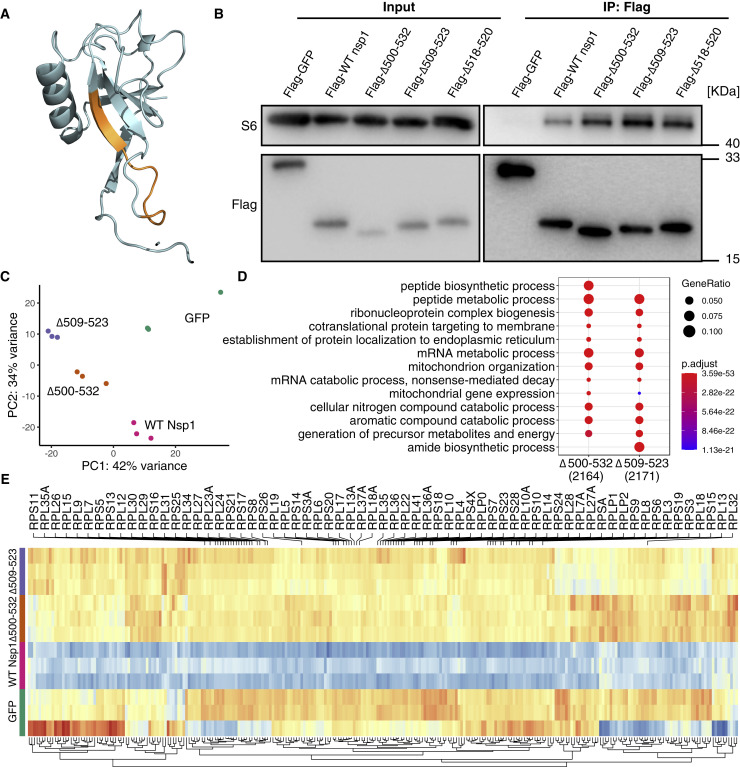
Figure 5.
Nsp1 mutants retained ribosomal binding ability while affecting mRNA metabolic process
(A) Mapping of 500-532 locus (A79PHGHVMVELV89, orange) onto the predicted 3D structure of N terminus of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 (Almeida et al., 2007; Wathelet et al., 2007).
(B) SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 mutant proteins bind to 40S ribosomal subunit. HEK293T cells were transfected with Nsp1-expressing (N-terminally tagged with FLAG) or control (FLAG-GFP) plasmid and immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody. Immunoblots were stained with anti-S6 or anti-FLAG antibodies.
(C) PCA (principal-component analysis) on transcriptome of Nsp1-expressing compared to GFP-expressing HEK239T cells.
(D) GO enrichment analysis of genes that were upregulated in the mutant compared to WT Nsp1-expressing cells.
(E) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes enriched in mRNA metabolic process. Genes coding for ribosomal proteins (RPs) were shown.