Figure 3.
SARS-CoV-2 infection results in severe lower respiratory tract pathology
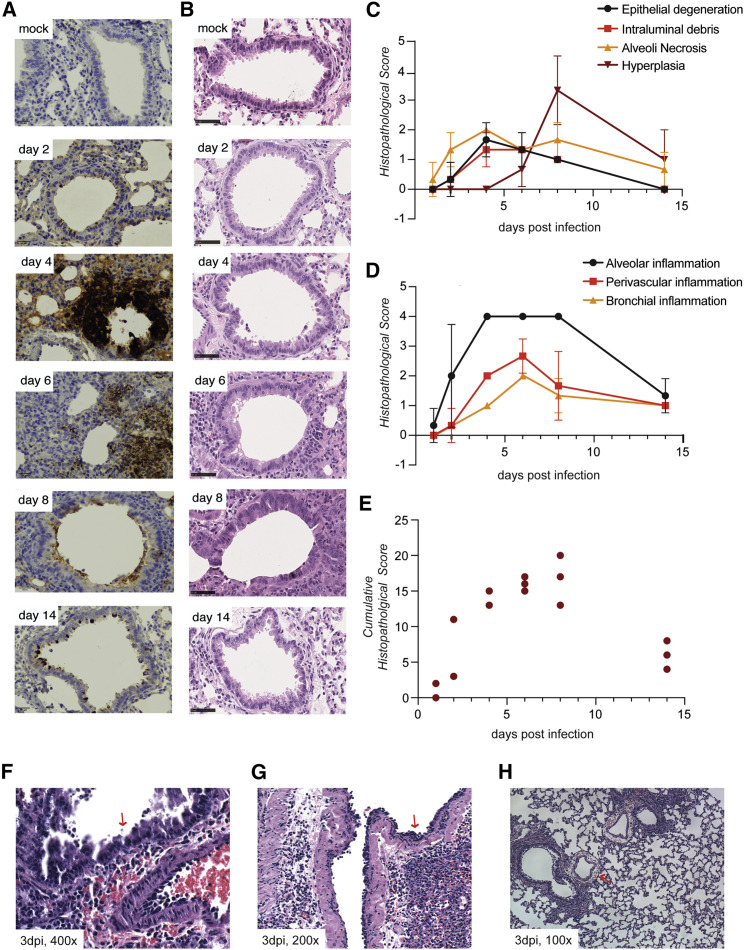
(A and B) Representative images of golden hamster lung tissue collected 2, 4, 6, 8, and 14 days after infection (100 PFUs) and immunohistochemistry with (A) N-specific antibody and (B) H&E (scale bar, 50 μm, n = 3).
(C and D) Average values of histopathological scores, assessed by a certified pathologist for each of the observations, corresponding to the time points in (A) and (B) (n = 3). Error bars indicate standard deviation.
(E) Cumulative clinical scores for nine different histopathological assessments (Table S2). Each point represents the score for one animal.
(F and G) Representative images of (F) apoptosis in the bronchial epithelium (400× magnification), (G) accumulation of neutrophils (200× magnification), and (H) severe vascular edema (100× magnification) in hamster lungs collected 3 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection (100 PFU).