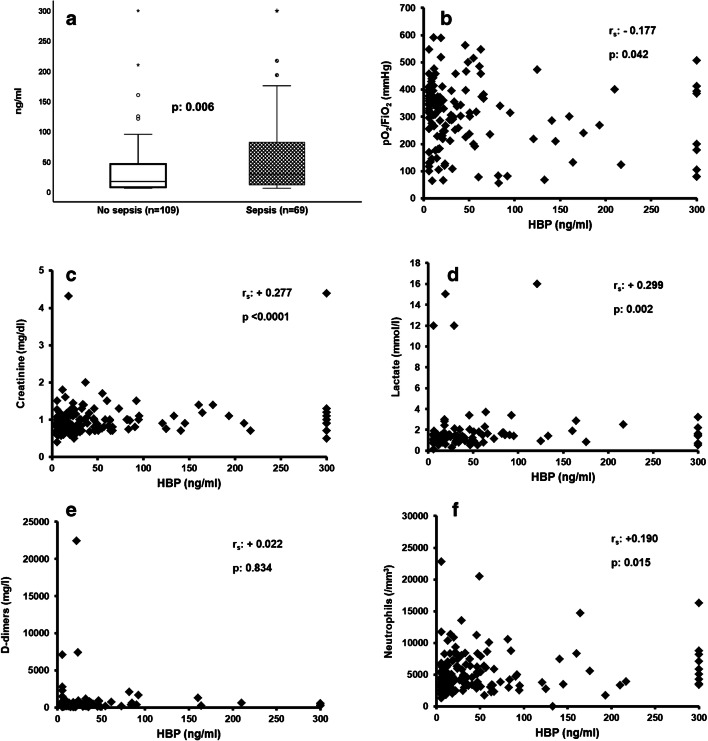
Fig. 1.
Association between heparin-binding protein (HBP) and organ dysfunction among patients with pneumonia by SARS-CoV-2. (a) Comparison of HBP between patients without sepsis by SARS-CoV-2 and sepsis by SARS-CoV-2; the p value of comparison by the Mann-Whitney U tests is provided. Circles denote outliers, and asterisk denotes extremes. (b) Correlation between HBP and pO2/FiO2; Spearman’s rank of correlation (rs) and the respective p value are provided. (c) Correlation between HBP and plasma creatinine; Spearman’s rank of correlation (rs) and the respective p value are provided. (d) Correlation between HBP and plasma lactate; Spearman’s rank of correlation (rs) and the respective p value are provided. (e) Correlation between HBP and plasma concentration of D-dimers; Spearman’s rank of correlation (rs) and the respective p value are provided. (f) Correlation between HBP and the absolute neutrophil count; Spearman’s rank of correlation (rs) and the respective p value are provided