Figure 4.
Proteomics Identifies a Critical Role of Ctf19cCCAN in Meiotic Kinetochore Assembly
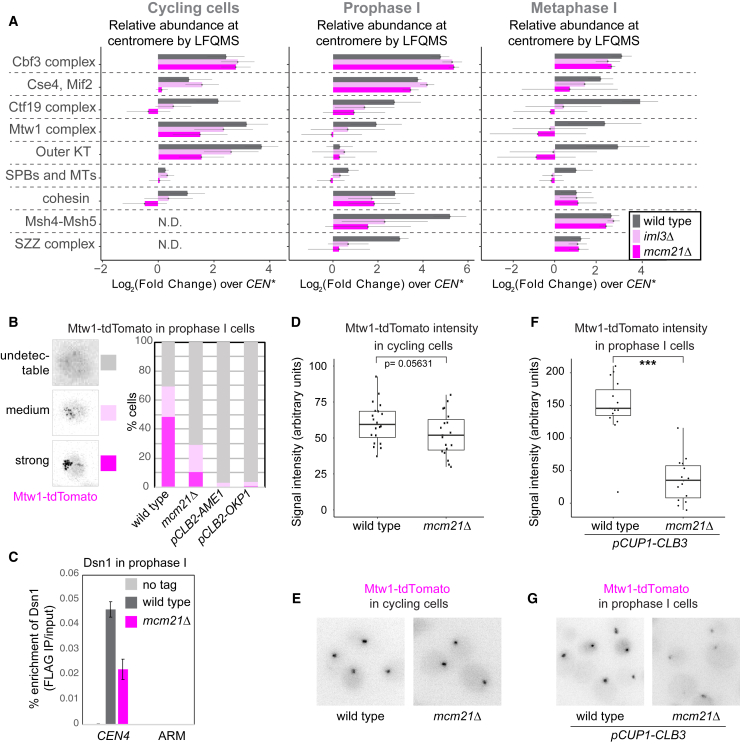
(A) Global CEN/CEN∗ proteomics reveals that kinetochore composition is altered in mcm21Δ and iml3Δ meiotic prophase I and metaphase I cells. The sum of LFQMS abundance of protein complexes on CEN chromatin in wild-type, iml3Δ, and mcm21Δ cells is shown as enrichment over CEN∗ chromatin isolated from wild-type cells. The abundance of Iml3 CENP-L and Mcm21CENP-O proteins was not included in the total Ctf19cCCAN count, as these proteins are missing in iml3Δ and mcm21Δ cells, respectively (STAR Methods). Error bars represent SD. KT, kinetochore; MT, microtubule; SPB, spindle pole body; SZZ, Spo16SPO16, Zip2SHOC1, Zip4TEX11.
(B–G) A functional Ctf19cCCAN is critical for Mtw1cMIS12c association with centromeres in meiotic prophase I, but not cycling cells.
(B) Wild-type, mcm21Δ, pCLB2-AME1, and pCLB2-OKP1 cells were imaged immediately after release from prophase I arrest. Representative images and scoring of cells with Mtw1-tdTomato signal are shown. n > 58 cells.
(C) Prophase I-arrested wild-type and mcm21Δ cells carrying ndt80Δ and DSN1-6His-3FLAG, together with untagged control, were subjected to anti-FLAG ChIP-qPCR. Error bars represent SE (n = 4 biological replicates). p < 0.05, paired t test.
(D–G) Mtw1-tdTomato signal intensity in cycling (D and E) and prophase I-arrested (F and G) wild-type and mcm21Δ cells. In (F) and (G), cells were engineered to ectopically produce Clb3 to maintain kinetochore clustering and allow signal quantification. In (D) and (F), whiskers represent 1.5 IQR, the middle line is median, and the box encompasses the two middle quartiles of the data. ∗∗∗p < 10−5; Mann-Whitney test. n > 19 (D) or n = 15 cells (F).
See also Figure S4.