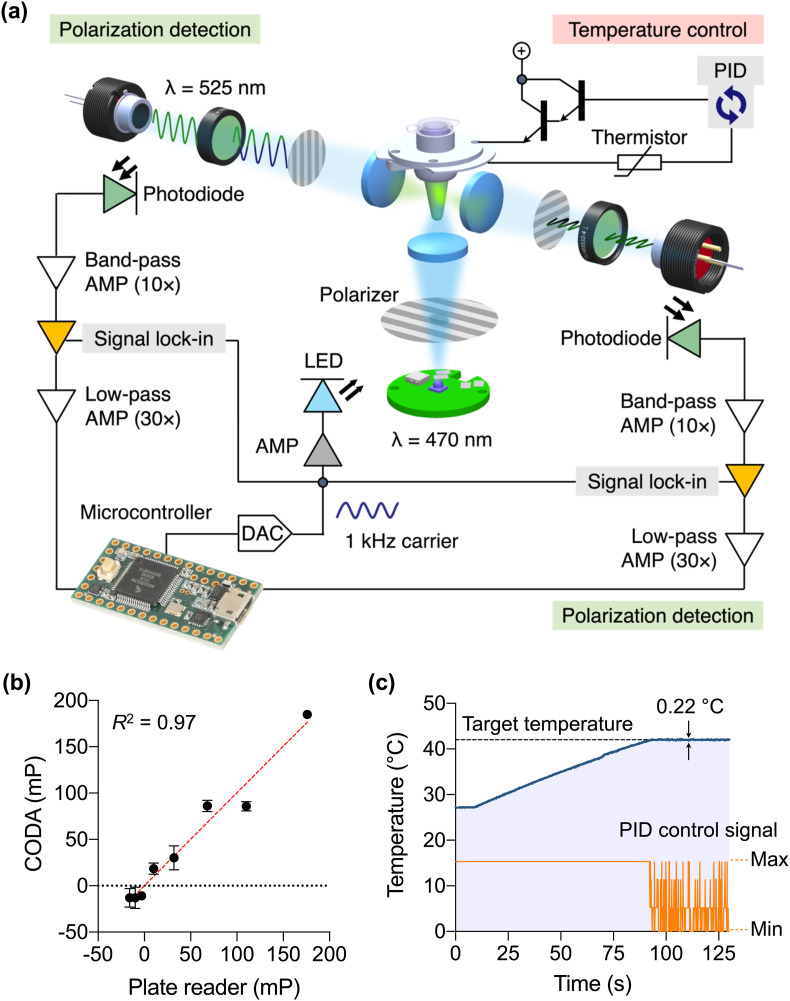
Fig. 2.
Optical design and validation of CODA device. (a) Optical and electrical schematic. A light emitting diode (LED) illuminates a sample with linearly polarized light oscillating at 1 kHz. Fluorescence is captured by two photodetectors, each consisting of a photodiode, a 525-nm bandpass filter and a linear polarizer. The signal is processed by a sequence of integrated filtering/amplification steps: 10 × bandpass, lock-in, and 30 × lowpass. The cleaned signals are finally captured by a microcontroller. Temperature is controlled through a feedback control. AMP, amplifier; DAC, digital-to-analog converter; PID, proportional–integral–derivative. (b) The CODA system was benchmarked against a conventional plate reader. Samples were prepared in triplicate through the serial dilution of glycerol in an aqueous buffer, varying the viscosity. All samples contained the same amount of fluorescein (240 nM). An excellent correlation was observed between these two systems. (c) Sample heating curve. The system reached the target temperature (42 °C) within 90 s. This temperature was maintained within ±0.2 °C variations.