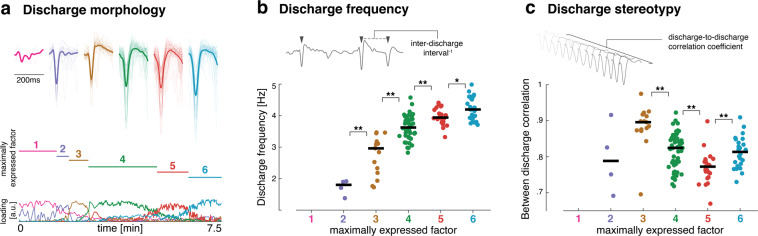
Fig. 6. Electrophysiological changes associated with ictal state transitions.
a Peak-centered averages of ictal discharges are shown for all discharges detected in a 10 s time window around the peak expression of each of the six sequential factors derived from NMF. Note that for visualization purposes, we show averages at a lower detection threshold, meaning that some fluctuations in the baseline are shown for comparison. For subsequent panels, thresholds were selected to not include baseline fluctuations in the detected discharges. b Ictal discharge frequency was estimated for nonoverlapping 3 s sliding windows labeled according to the factor that was maximally expressed during the time window. This shows progressive increases in ictal discharge frequency for the duration of the seizure. c Stereotypy of ictal discharges was measured by calculating for each channel the between-discharge correlation for all discharges identified within a 3 s sliding window. This shows that discharges are very stereotyped early in the seizure and become most heterogeneous around the expression of factor 5. Across panels n = 121 ictal discharges (mean 24 per factor, range 7–52).