Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of the chemical posttranslational modification for in vitro ribosomal synthesis of azole-containing peptides.
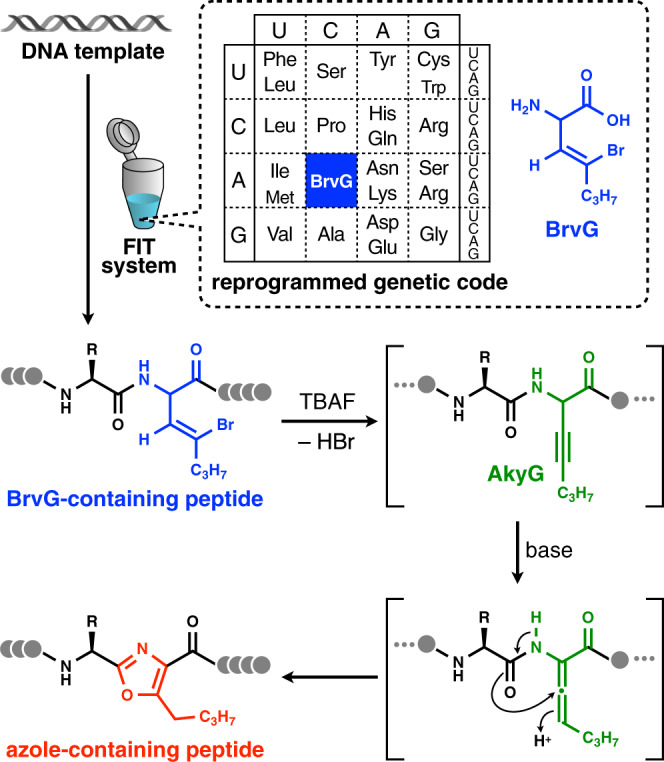
For posttranslational installation of azoles into translated peptides, a 4-bromovinylglycine derivative (BrvG, shown in blue) is incorporated into the nascent peptide chain via genetic code reprogramming. Subsequent treatment of the expressed peptide with tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) induces dehydrobromination to give the corresponding β,γ-alkynylglycine derivative (AkyG, shown in green), which spontaneously undergoes isomerization to produce an azole ring (shown in red) in the peptide backbone.
