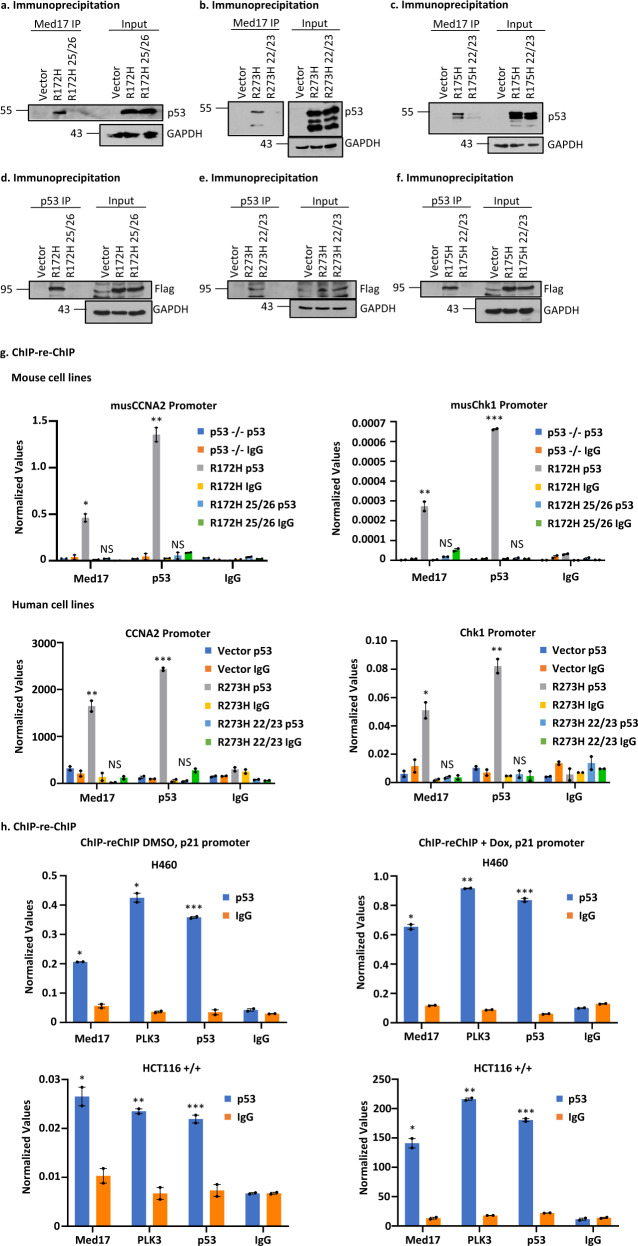
Fig. 4. GOF p53 interacts with Med17 and amino acid acids at mouse p53 L25, W26 (L22, W23 in human) are important for this interaction.
a Immunoprecipitation experiment showing complex formation between murine p53-R172H and the Mediator protein 17 (Med17) in solution. Nuclear extracts were made from murine lung cells expressing p53-R172H (generated by adeno Cre as described in the text), p53-L25Q/W26S/R172H, and control, and immunoprecipitated by Med17 antibody and probed with anti-p53 antibody. b Immunoprecipitation experiment showing complex formation between p53-R273H with Med17 in solution. Nuclear extracts were prepared from H1299 cells stably transfected with empty vector, expressing p53-R273H and -L22Q/W23S/R273H, and immunoprecipitated by Med17 antibody and probed with anti-p53 antibody. c Immunoprecipitation experiment showing complex formation between p53-R175H and Med17 in solution. Nuclear extracts were prepared from H1299 cells stably transfected with empty vector, expressing p53-R175H and -L22Q/W23S/R175H, and immunoprecipitated by Med17 antibody and probed with anti-p53 antibody. d Reverse immunoprecipitation experiment showing complex formation between murine p53-R172H and the Mediator protein 17 (Med17) in solution. Whole cell extracts were made from murine lung cells expressing p53-R172H (generated by adeno Cre as described in the text), p53-L25Q/W26S/R172H, and control after transfection with Flag-Med17, and immunoprecipitated by p53 antibody and probed with anti-Flag antibody. e Reverse immunoprecipitation experiment showing complex formation between p53-R273H and the Mediator protein 17 (Med17) in solution. Whole cell extracts were made from H1299 cells stably transfected with empty vector, expressing p53-R273H and -L22Q/W23S/R273H after transfection with Flag-Med17, and immunoprecipitated by p53 antibody and probed with anti-Flag antibody. f Reverse immunoprecipitation experiment showing complex formation between p53-R175H and the Mediator protein 17 (Med17) in solution. Whole cell extracts were made from H1299 cells stably transfected with empty vector, expressing p53-R175H and -L22Q/W23S/R175H after transfection with Flag-Med17, and immunoprecipitated by p53 antibody and probed with anti-Flag antibody. g ChIP-re-ChIP experiment showing complex formation on mutant p53 inducible gene promoters (cyclin A2 and chk1) between mutant p53 and Med17. ChIP-re-ChIP was carried out as described using murine lung cells described in a and H1299 cells described in b. The first immunoprecipitation was carried out with p53 antibody, while the second one was done using a Med17 antibody. Presence of promoter sequences was detected by QPCR using promoter specific primers. Data are normalized with input DNA values for each respective promoter and is presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). A two-sided Student’s t-test was performed; Mouse CCNA2 *p = 0.009, **p = 0.003, Mouse Chk1 **p = 0.007, ***p = 3.12E–5; Human CCNA2 **p = 0.008, ***p = 0.0002, Human Chk1 *p = 0.01, **p = 0.005. h ChIP-re-ChIP experiment showing complex formation on wild-type (WT) p53 inducible gene promoter p21 between WT p53 and Med17. ChIP-re-ChIP was carried out as described using H460 (WT p53) and HCT116 (p53+/+). The first immunoprecipitation was carried out with p53 antibody, while the second one was done using a Med17 antibody. Presence of promoter sequences was detected by QPCR using promoter specific primers. Data are normalized with input DNA values and is presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). A two-sided Student’s t-test was performed; H460 DMSO *p = 0.001, ***p = 0.0007; H460 Dox *p = 9.6E–4, **p = 1.05E–5, ***p = 2.29E–4; HCT116+/+ DMSO *p = 0.02, **p = 0.006, ***p = 0.009, HCT116+/+ Dox *p = 0.004, **p = 6.3E–5, ***p = 2.2E–4. Assay was performed with or without Dox treatment. NS no statistically significant difference from control.