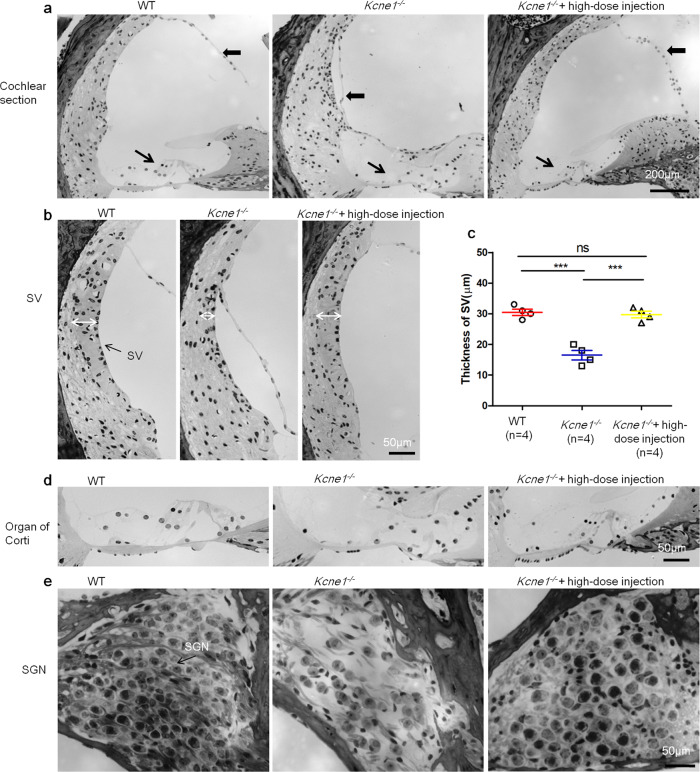
Fig. 5. Morphologies of cochlear sections in the middle turn of WT, untreated, and high-dose-treated Kcne1−/− mice observed at P30 (n = 4 in each group).
a Comparison of the morphology of the cochlear section of WT, untreated, and high-dose-treated Kcne1−/− mice. b Comparison of the thickness of the stria vascularis (SV) in the middle turn of the WT, untreated, and high-dose-treated Kcne1−/− mice. c Quantitative comparison of the thicknesses of the SV in the WT, untreated, and high-dose treated Kcne1−/− mice (n = 4 in each group, p = 0.0003 in WT ears and p = 0.0004 in treated Kcne1−/− ears, comparing to untreated Kcne1−/− ears, two-sided Student’s t tests). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ***: p < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source data file. d Comparison of the morphology of the organ of Corti of the WT, untreated, and high-dose-treated Kcne1−/− mice. e Comparison of the morphology of spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) in the middle turn of the WT, untreated, and high-dose-treated Kcne1−/− mice. Heavy black arrows point to the Reissner’s membrane. Fine black arrows point to the organ of Corti. White double-headed arrows indicate the border for measuring the thickness of the SV.