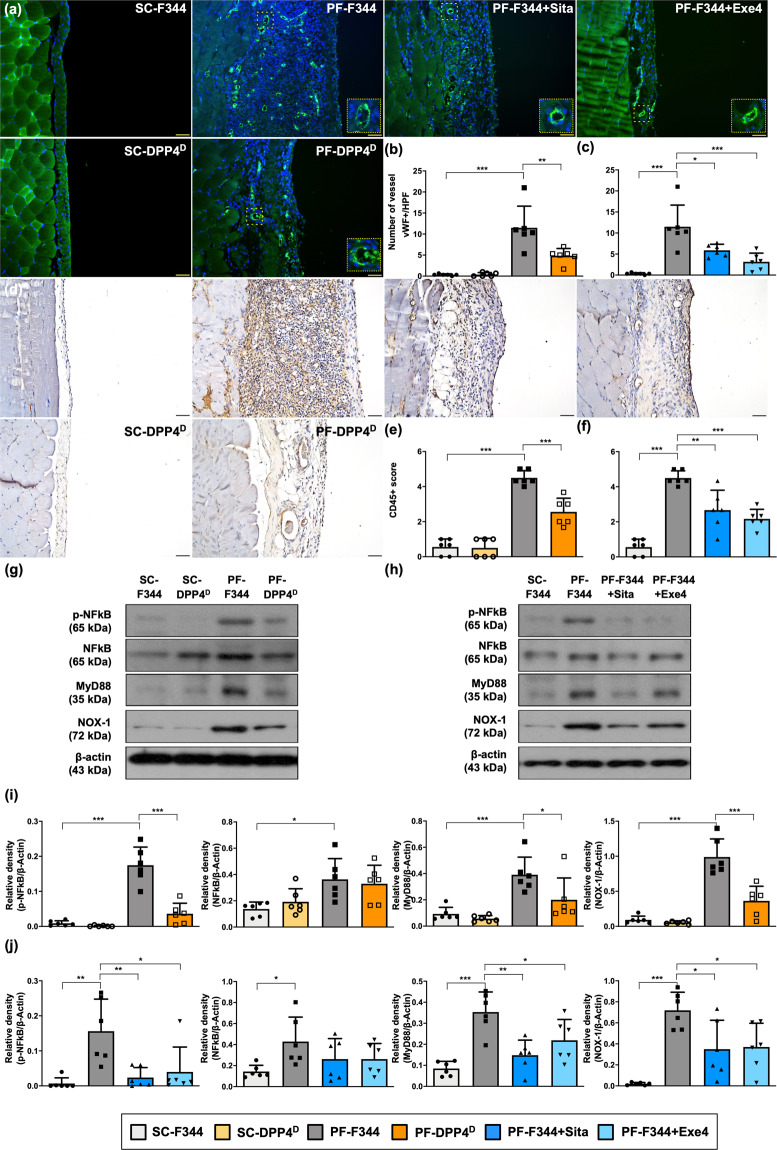
Fig. 6. DPP4 deficiency, sitagliptin, and exendin-4 ameliorated CG-inducing angiogenesis and inflammation by suppressing NF-κB/MyD88 signaling in rats.
a Representative images of vessels in peritoneal tissue on day 21 were detected by immunofluorescent staining (200×) in each group. The blood vessels were indicated by round vWF positive signal (green color). DAPI labels cellular nuclei (blue color). Scale bars: 50 μm. b, c Quantitative number of vessels as vWF+ per high-power field (HPF) in each group. d Illustrating images (200×) of each group for identification of positively stained CD45 (brown color) as the leukocyte marker by immunohistology staining in peritoneal tissue after CG-inducing PF on day 21. Scale bars: 50 μm. e, f Quantitative of CD45+ score in each group. g, h Western blotting was performed to detect the protein levels of p-NF-kB, NF-kB, MyD88, and NOX-1 in the peritoneal tissues of each group. i, j Quantitative results of Fig. 6g and Fig. 6h were shown, respectively. n = 6 for each group. Data represents mean ± SD; * indicates p-value <0.05; ** represents p-value <0.01; and *** is p-value <0.001.