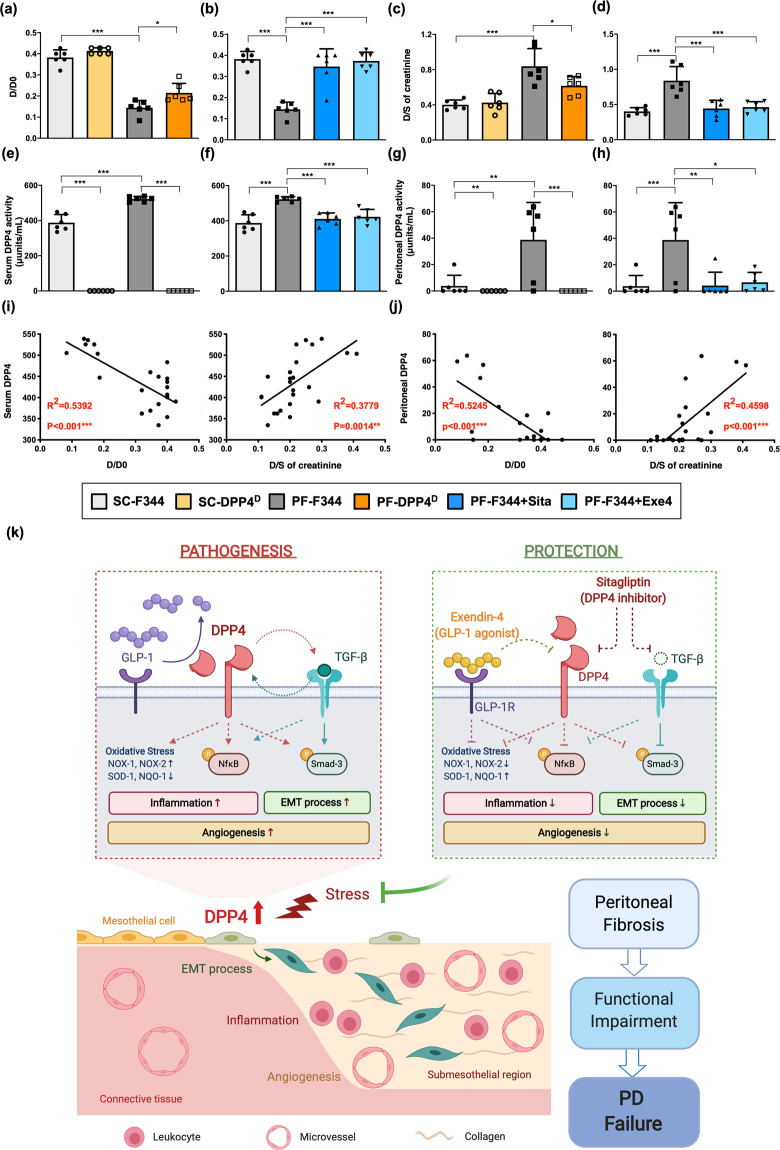
Fig. 7. DPP4 deficiency, sitagliptin, and exendin-4 reduced the functional impairments of peritoneal membrane with peritoneal fibrosis in rats.
After CG-inducing PF, both F344 wild-type (F344) and DPP4 deficiency (DPP4D) rats were injected with dialysate (4.25% Dianeal) at 100 ml/kg body weight to evaluate the peritoneal equilibration test (PET) for assessment of peritoneal membrane transport function. a, b After injecting dialysate for 1 h, the peritoneal absorption of glucose from the dialysate was monitored the ratio of peritoneal glucose uptake at the end of the test compared to the initiation (D/D0). c, d Dialysate-to-Serum (D/S) ratio of creatinine was assessed after injecting dialysate for 4 h. e, f DPP4 activity in serum among groups. g, h DPP4 activity in peritoneal fluids among groups. i In wild-type rats, the correlations between the DPP4 activity in serum and the parameters of peritoneal transport, D/D0 and D/S creatinine, were evaluated. j In wild-type rats, the correlations between the DPP4 activity in peritoneal fluids and the parameters of peritoneal transport were calculated. n = 6 for each group. Data represents mean ± SD; * indicates p-value <0.05; ** represents p-value <0.01; and *** is p-value <0.001. k The schematic illustrating the DPP4 role involving in the pathogenetic progression of peritoneum to PD failure, which was established from our experimental results and clinical observation. During glucose exposure or CG-inducing injury, DPP4 was upregulated and degraded active GLP-1. Meanwhile, DPP4 exhibited the crosstalk with TGF-β to further trigger EMT process via SMAD3 pathway. On the other hand, DPP4 upregulation induced the oxidative stress generation and activation of NFκB, pathway followed by attract inflammatory cell infiltration. Both inflammation and EMT progressed angiogenesis as well as caused collagen deposition, peritoneal fibrosis, functional impairment, and finally PD failure. Importantly, the incretin-based therapy, including sitagliptin and exendin-4, effectively protected peritoneal integrities and improved the peritoneal impairments. This schematic was created with BioRender.com. EMT epithelial–mesenchymal transition, PD peritoneal dialysis.