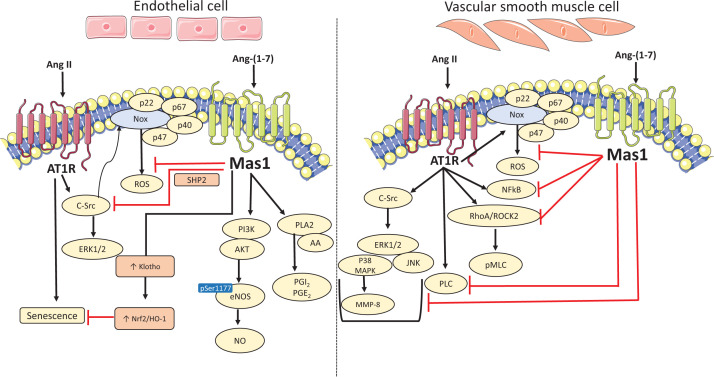
Figure 3. Vascular signalling of Ang-(1-7)/Mas1 in endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells.
In endothelial cells, Ang-(1-7) activates eNOS via AKT to produce nitric oxide. Ang-(1-7) also stimulates production of vasodilators such as prostacyclin (PGI2) and prostaglandin (PGE2) via enhancement of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity and arachidonic acid (AA) release. Ang-(1-7) via Mas1 counter-regulates Ang II effects by increasing expression of anti-ageing protein klotho which consequently activates Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and activation of c-Src, ERK1/2 and NADPH oxidase (Nox) by enhancing SHP-2 phosphorylation. In smooth muscle cells, Ang-(1-7) via Mas1 receptor opposes Ang II-induced contraction and oxidative stress by attenuating RhoA/ROCK2 signalling, PLC and NADPH activation. Ang-(1-7) also suppresses Ang II-induced proliferation and inflammation by inhibiting MAPKs (ERK1/2, p38MAPK and JNK), MMP-8 and NFκB signalling. AKT, serine threonine specific protein kinase; Ang II, angiotensin II; Ang-(1-7), angiotensin-(1-7); AT1R, angiotensin two type one receptor; ERK1/2, extracellular regulated kinase one and two; HO-1, haem oxygenase one; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; Mas1, mas1 receptor; MMP-8, matrix metalloproteinase 8; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NFkB, nuclear factor kappa B; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PLC, phospholipase C; RhoA/ROCK2, RAAS homolog family member A/Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SHP-2, small heterodimer partner 2.