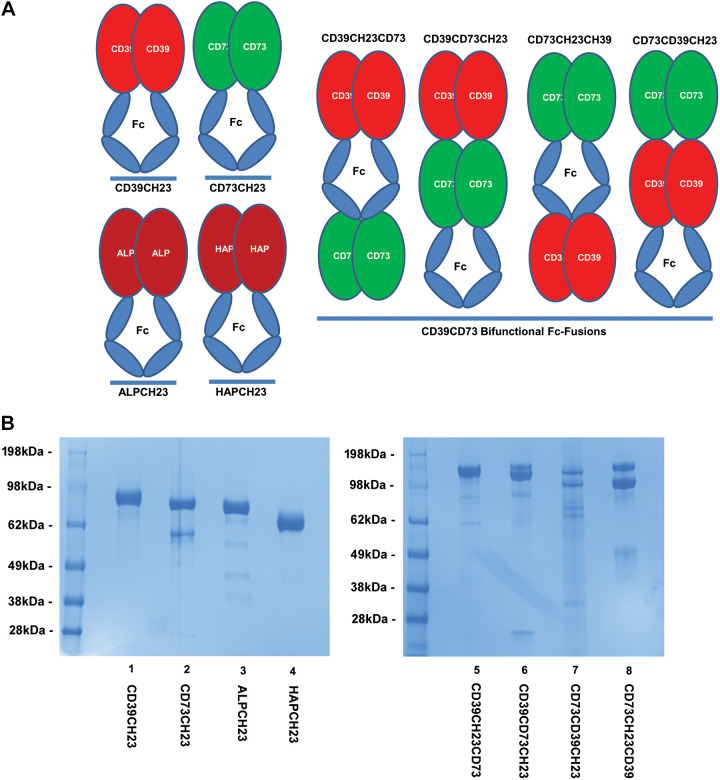
Figure 1.
Engineering novel bifunctional fusions of CD39-CD73 and control fusion proteins. A: novel CD39-CD73 bifunctional chimeric proteins were bioengineered by fusing the ectodomain (ECD) of human CD39 and CD73 to either the NH2- or COOH-terminus of the Fc region of human IgG1 and to the other domain through gene synthesis and PCR cloning, as described in materials and methods. To generate activity comparison controls, human CD39-ECD-Fc fusion (CD39CH23), human CD73-ECD-Fc fusion (CD73CH23), human alkaline phosphatase ECD-Fc fusion (ALPCH23), and human acid phosphatase ECD-Fc fusion (HAPCH23) were also generated through gene synthesis and PCR cloning, as described in materials and methods. B: production of CD39-CD73 bifunctional fusions and the control fusion proteins. The resulting constructs shown in A were then transfected into Expi293F cells as described in materials and methods. Chimeric recombinant proteins, secreted into conditioned media, were affinity-purified through protein A resin and buffer-exchanged, as described in materials and methods. As described, 4 µg of protein samples was run, under reduced conditions, on 4%–12% SDS-PAGE and then stained with Coomassie blue. SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.