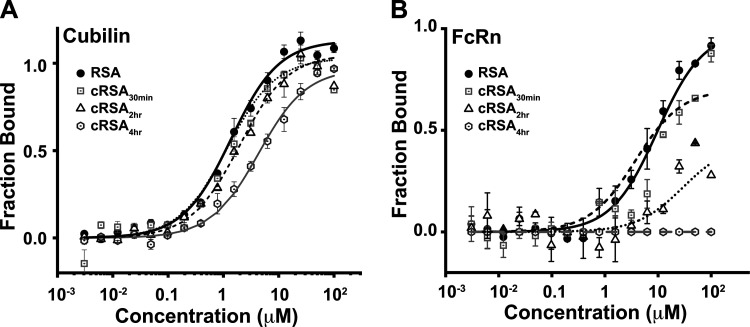
Figure 6.
Carbamylation reduces rat serum albumin (RSA) binding affinity to both cubilin (A) and FcRn (B). Microscale thermophoresis (MST) was used to characterize albumin-binding affinity between purified cubilin (CUB7,8 domain) or FcRn. Binding assays were performed with the Monolith NT.115 microscale thermophoresis device using standard capillaries (NanoTemper Technologies, Munich, Germany). Measurements were performed at 25°C in 67 mM NaPO4 buffer, 150 mM NaCl, and 0.05% Tween 20 at pH 6.0 (for FcRn binding) or 7.4 + 1 mM CaCl2 (for cubilin binding). Data from a minimum of three replicate binding assays were analyzed using NanoTemper analysis and GraphPad Prism or Origin software. Means ± SD are presented. A progressive loss of albumin binding was measured for both cubilin (0.5 µM to >15 µM) and FcRn (10 µM to >100 µM) as carbamylation increased.