Figure 10.
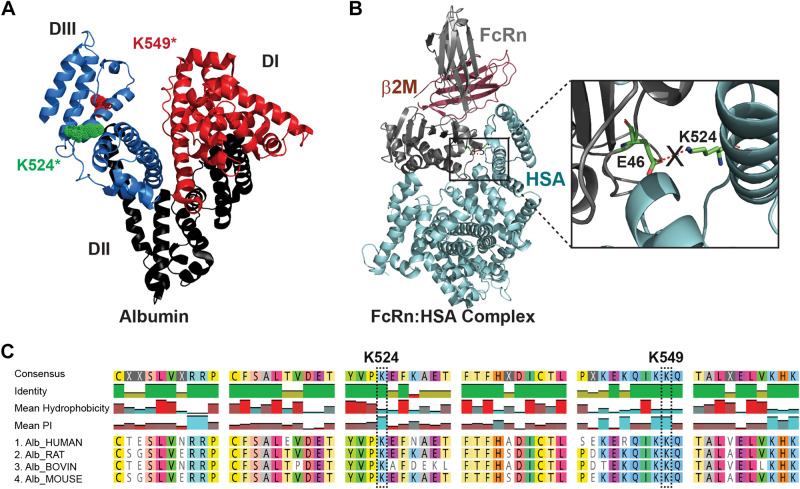
Carbamylation at the K524 site in rat serum albumins (RSA) blocks the critical salt bridge interaction essential to form the FcRn-albumin binding complex. The combined approach of analyzing in silico analysis of FcRn-HSA crystal structure and LC-MS/MS data of digested peptides of carbamylated albumins was done to address the mechanism of reduced binding to FcRn. The albumin crystal structure PDB ID 1E78 showed all three domains of albumin, along with the highest carbamylation site K549* and critical site K524* located in domain III, as observed in MS/MS analyses (A). The crystal structure of FcRn and serum albumin PDB ID 4N0F is shown in B. The enlarged view shows the critical salt bridge between the E46 residue of FcRn and K524 of albumin necessary for their interaction, which is blocked when K524 is carbamylated (B). Multiple-sequence alignment data from Clustal Omega (C) showed that these sequences and key lysines are highly conserved in mammals, so carbamylation at this site will affect the albumin FcRn interaction, albumin transcytosis, and thus metabolism. Note that the interacting residue for the FcRn-RSA crystal structure (PDB ID 4N0F) analyzed by PDBsum EMBL-EBI and numbering of residues K549* is the same as in Ref. 3, whereas K524* is same as K500 as numbered in the crystal structure PDB ID 4N0F (4). HSA, human serum albumin.