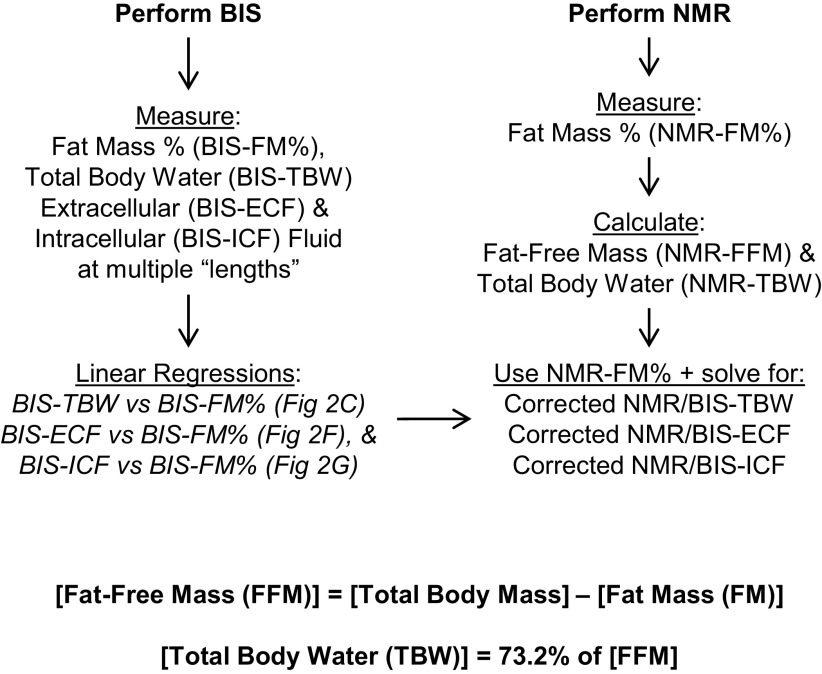
Figure 1.
Workflow of combined NMR/BIS methodology. Fluid compartmentalization is analyzed using BIS, and body composition is analyzed using time-domain NMR. From BIS analyses, fat mass, total body water, extracellular, and intracellular fluid volumes are determined at multiple theoretical “lengths.” Linear regressions are then performed to associate calculated fluid compartment sizes and fat mass against theoretical “length” values. Because these relationships are demonstrably linear (i.e., see Fig. 2, A, B, D, and F), substitution methods are then used to associate calculated fluid compartment sizes with calculated fat mass values within each animal (i.e., see Fig. 2, C, E, and G). NMR-based assessments of body composition, including fat mass, fat-free mass, and total body water, are then used to solve for corrected fluid compartment sizes for each animal (i.e., see Fig. 2, E and G). BIS, bioimpedance spectroscopy; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance.