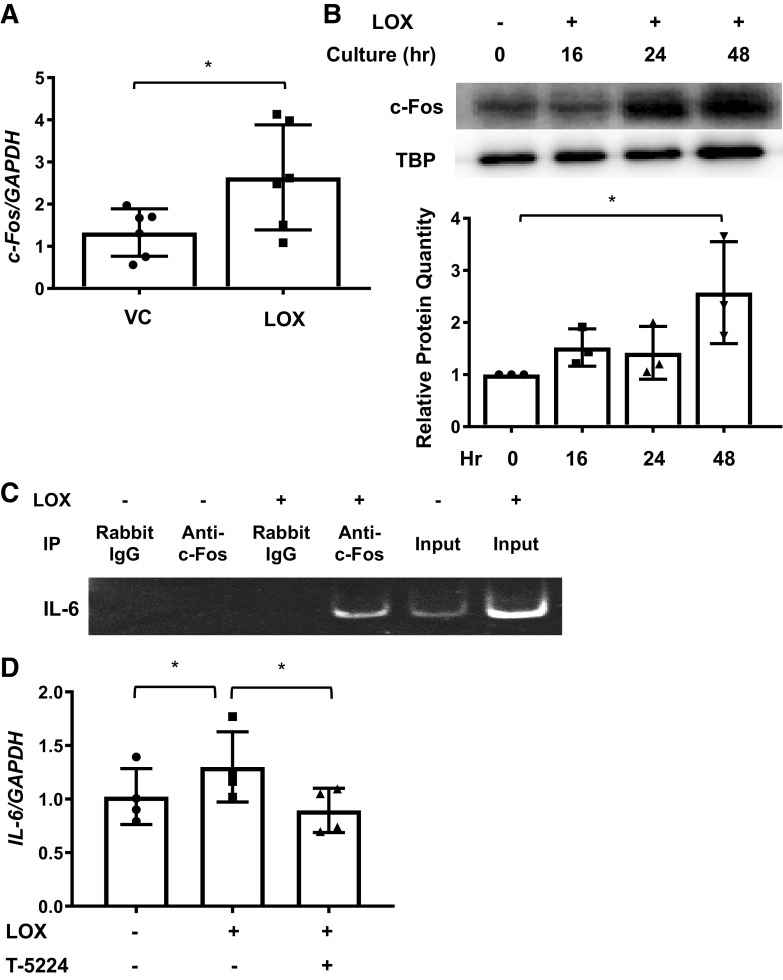
Figure 7.
Lysyl oxidase (LOX) induces c-Fos expression. A: mRNA were extracted from human primary lung fibroblasts treated with recombinant LOX (LOX) or vehicle (VC) for 16 h. Expression of c-Fos was evaluated using real-time PCR. The data were obtained from six different experiments using fibroblasts from lung tissues of six different individual donors. Graphical presentation of the data analyzed by paired t test. Values represent means ± SD. *P < 0.05. B: an equal number of human primary lung fibroblasts were treated with LOX at 0, 16, 24, and 48 h. Protein levels of c-Fos from the nuclear fraction were assessed by immunoblotting. Top: c-Fos in nuclear fractions from an equivalent number of fibroblasts was detected by immunoblotting and signals were normalized to TATA-box binding protein (TBP) at the bottom. Graphical presentation of the data from three different experiments using fibroblasts from lung tissues of three different individual donors and analyzed using ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s test. Values represent means ± SD. *P < 0.05. C: an equal number of human primary lung fibroblasts were treated with LOX or vehicle (VC) for 48 h and coimmunoprecipitation of c-Fos and IL-6 promoter were performed. The samples were visualized on a polyacrylamide gel. D: primary human lung fibroblasts were treated with LOX in the presence or absence of c-Fos inhibitor (T-5224) for 48 h. Expression of IL-6 was evaluated using real-time PCR. The data were obtained from four different experiments using fibroblasts from lung tissues of four different individual donors. Comparison among three or more groups was performed using ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s test. Values represent means ± SD. *P < 0.05.