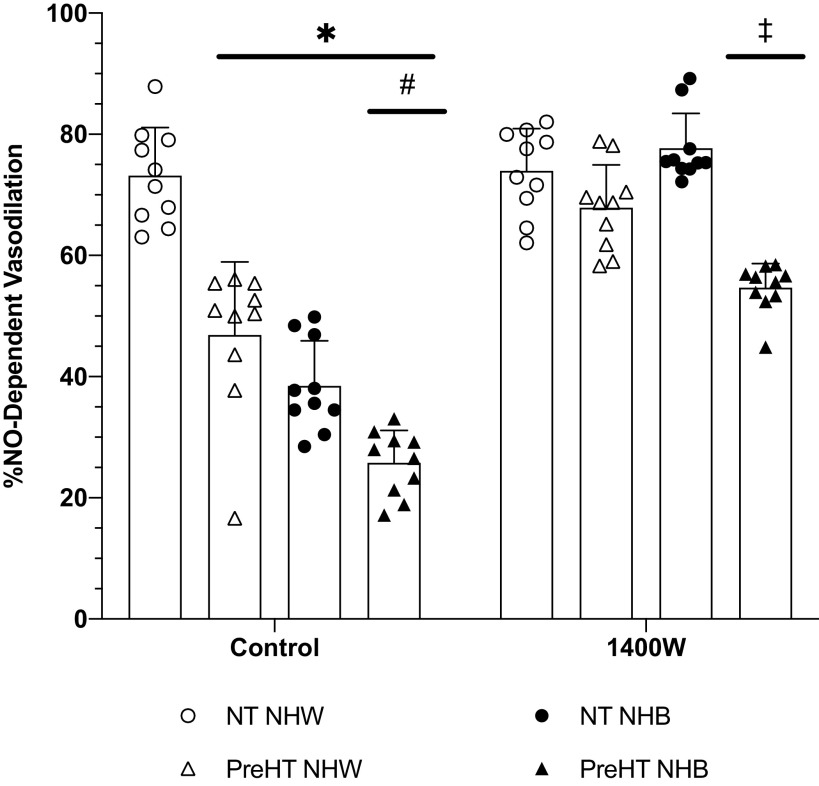
Figure 5.
Calculated % nitric oxide (%NO)-dependent vasodilation. Group responses are shown as means ± SD and were compared with a 3-way ANOVA. At control sites, %NO-dependent vasodilation was significantly reduced in prehypertensive non-Hispanic Whites (PreHT NHW; n = 10 participants), normotensive non-Hispanic Blacks (NT NHB; n = 10 participants), and prehypertensive non-Hispanic Blacks (PreHT NHB; n = 10 participants) relative to normotensive non-Hispanic Whites (NT NHW; n = 10 participants). The %NO-dependent vasodilation at control sites in PreHT NHB was significantly reduced compared to PreHT NHW and NT NHB. At 1400W sites, %NO-dependent vasodilation was restored in both PreHT NHW and NT NHB. The %NO-dependent vasodilation at 1400W sites was increased in PreHT NHB, but this was reduced relative to all other groups. *P < 0.05 vs. NT NHW; #P < 0.05 vs. PreHT NHW and NT NHB; ‡P < 0.05 vs. NT NHW, PreHT NHW, and NT NHB.