Figure 10. Analysis of the replication efficiency of JCV Agno (15-71) mutant virus (with no MTS).
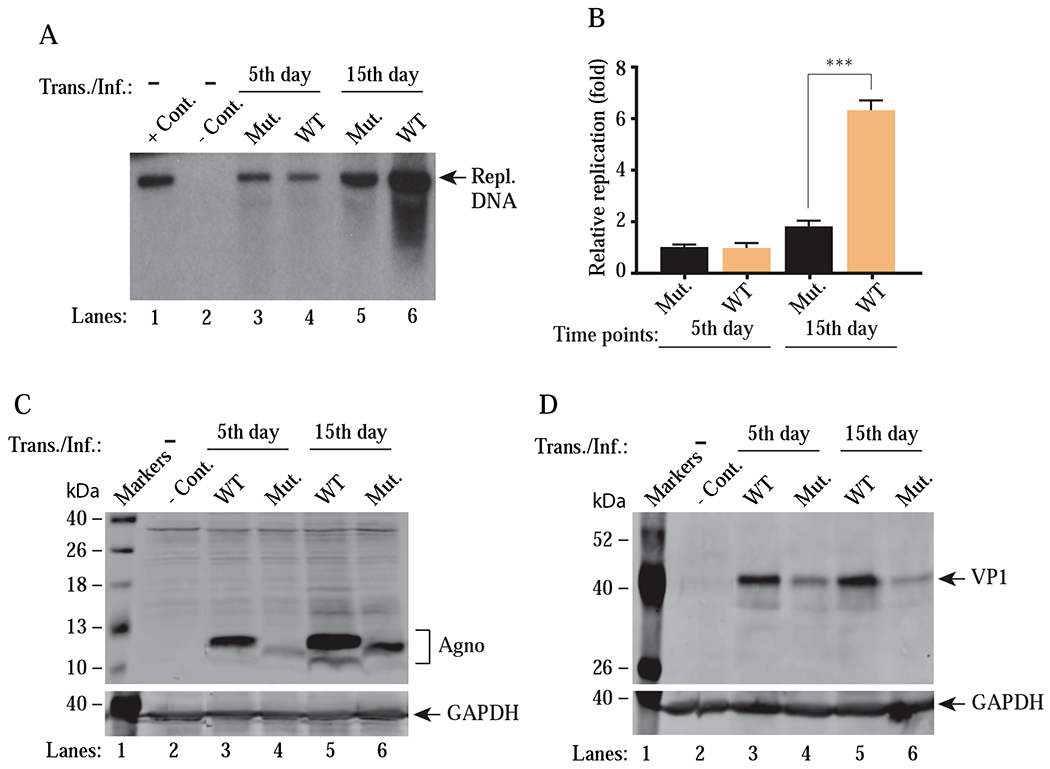
(A) Southern blot analysis of replicated viral DNA. The plasmid constructs [Bluescript KS-JCV Mad-1 WT (WT) and Bluescript KS-JCV Mad-1 Agno (15–71) mutant (Mut.)] were digested with BamHI to liberate the viral genome from the vector and then were separately transfected/infected into SVG-A cells using lipofectamine™ 3000 according to manufacturer’s recommendations. At the indicated time points, the low-molecular-weight DNA containing both input and replicated viral DNA was isolated and digested with BamHI and DpnI restriction enzymes and Southern blot analysis was performed as described in materials and methods. In lane 1, 6 ng of purified JCV Mad-1 WT DNA linearized by BamHI digestion was loaded as positive control (+ Cont.). In lane 2, DNA isolated from the uninfected cells was treated as a negative control (− Cont.). Replication assays were performed in duplicates and a representative data is shown here. (B) Quantitation analysis of Southern blots by a semi-quantitative densitometry method (using NIH Image J program) and presentation of the results in arbitrary units (relative fold replication). Results were statistically analyzed by GraphPad program using One-way ANOVA and data columns were compared by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. *** indicates a significant difference with respect to replication rates between WT and mutant at 15th day posttransfection/infection, (P < 0.0001). (C and D) Western blot analysis of whole-cell extracts prepared from the SVG-A cells, transfected/infected with either WT or mutant [Agno (15-71)] virus to assess the Agno (C) and VP1 (D) levels using α-Agno and α-VP1 (Dugan et al., 2007) antibodies. GAPDH was used as a loading control and detected α-GAPDH antibody (Santa Cruz, catalog no. sc-47724) by Trans./Inf.: Transfection/Infection.
