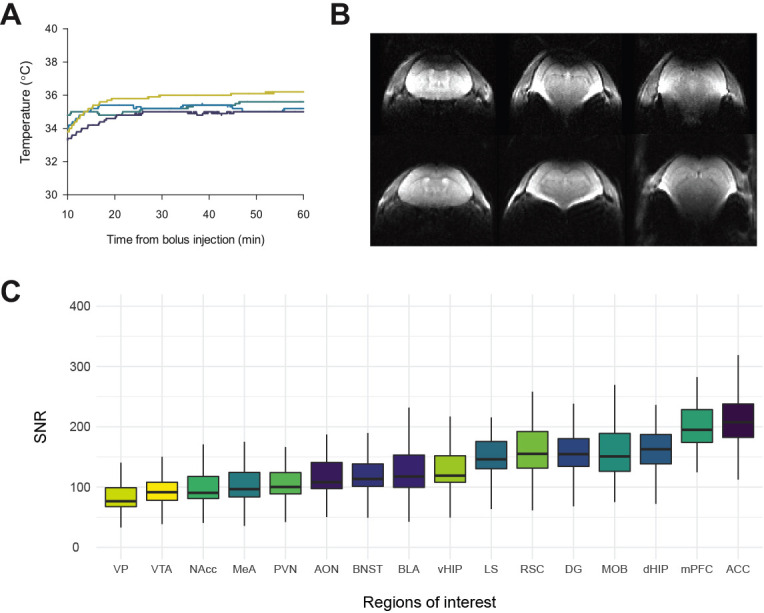
Figure 1. Experimental design and brain regions of interest.
(A) Sequence of experiments during a 30 day period: Female voles were bilaterally ovariectomized before MR and behavioral protocols. After being allowed to recover from surgery for 10 days, silastic capsules containing E2B (estradiol benzoate) were implanted via s.c. 4 days before cohabitation for sexual receptivity induction. Once couples went under cohabitation, they were housed together for the rest of the experiment and were only separated for PPT and MR scanning sessions. OVX: ovariectomy surgery. MR: magnetic resonance imaging scanning session. PPT: partner preference test. (B) Regions of interest (ROIs) for network functional connectivity analyses. Antero-posterior coronal slices of the prairie vole template overlayed with ROI masks with the resolution used in the analysis. Each color represents a different ROI. ACC: anterior cingulate cortex. AON: anterior olfactory nucleus. BLA: basolateral amygdala. BNST: bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. DG: dentate gyrus. dHIP: dorsal hippocampus. MeA: medial amygdala. MOB: main olfactory bulb. LS: lateral septum. mPFC: medial prefrontal cortex. NAcc: nucleus accumbens. PVN: paraventricular nucleus. RSC: retrosplenial cortex; VP: ventral pallidum. vHIP: ventral hippocampus. VTA: ventral tegmental area. (C) 3D views of ROI masks embedded within the prairie vole template.
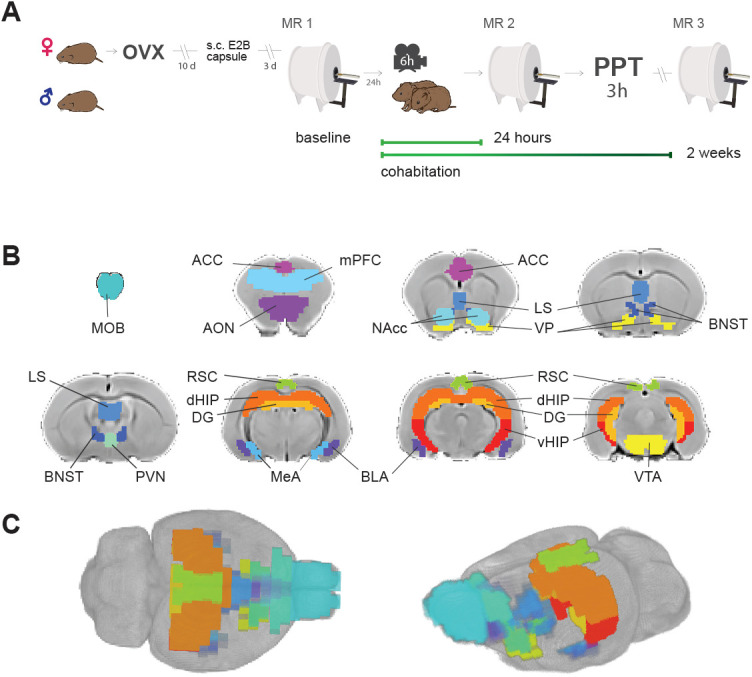
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Representative rsfMRI time series.
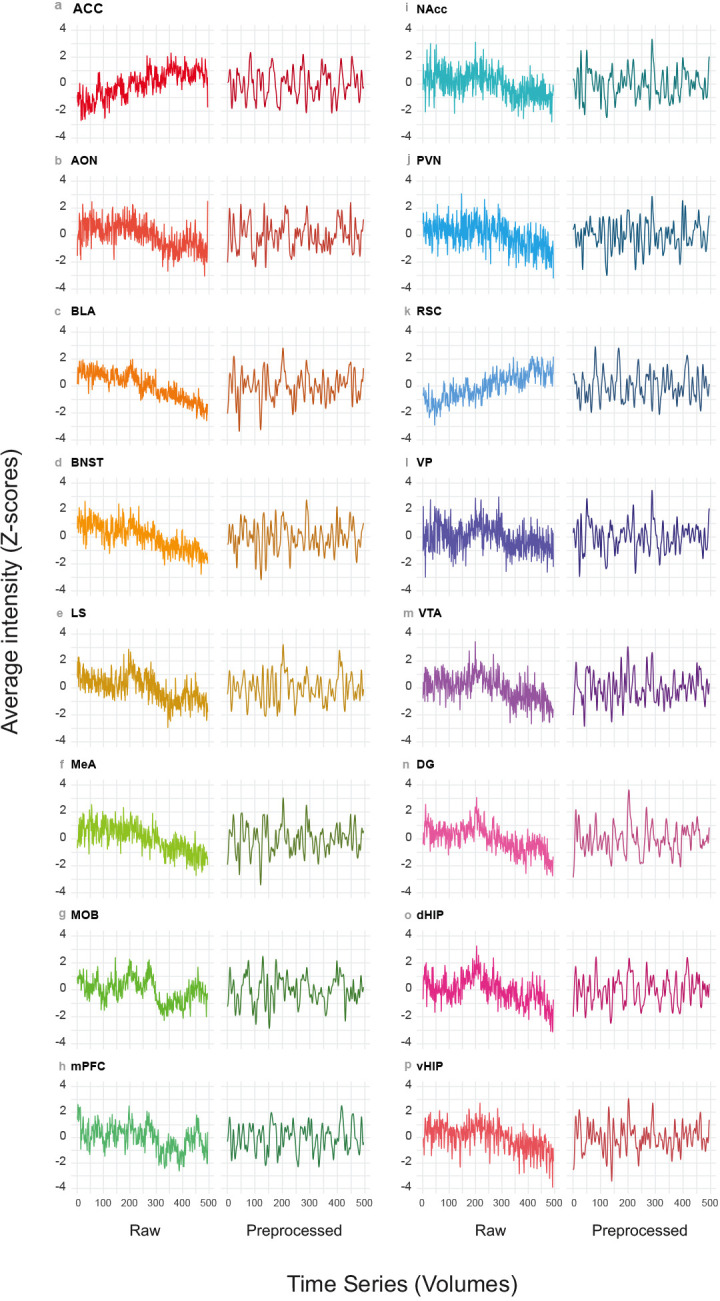
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Average functional connectivity correlation matrices between ROIs in all subjects shown by MR acquisition sessions: baseline, 24 hr, and 2 weeks.
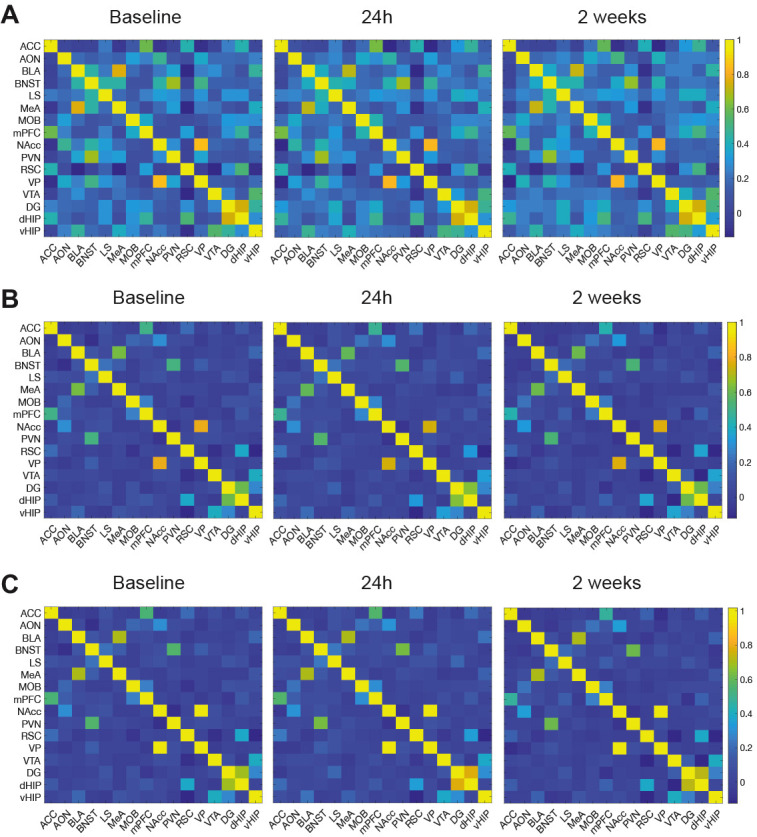
Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Representative rsfMRI and anatomical raw data and examples of the registration steps.
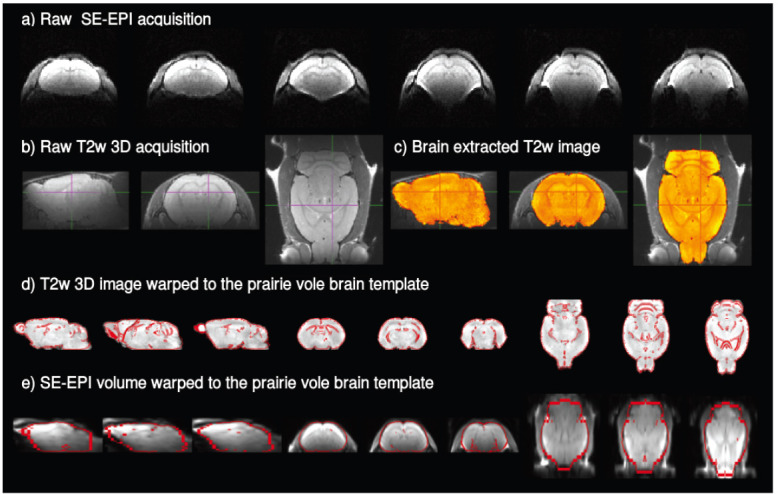
Figure 1—figure supplement 4. Average seed-based functional connectivity maps for each of the 16 ROIs here explored.
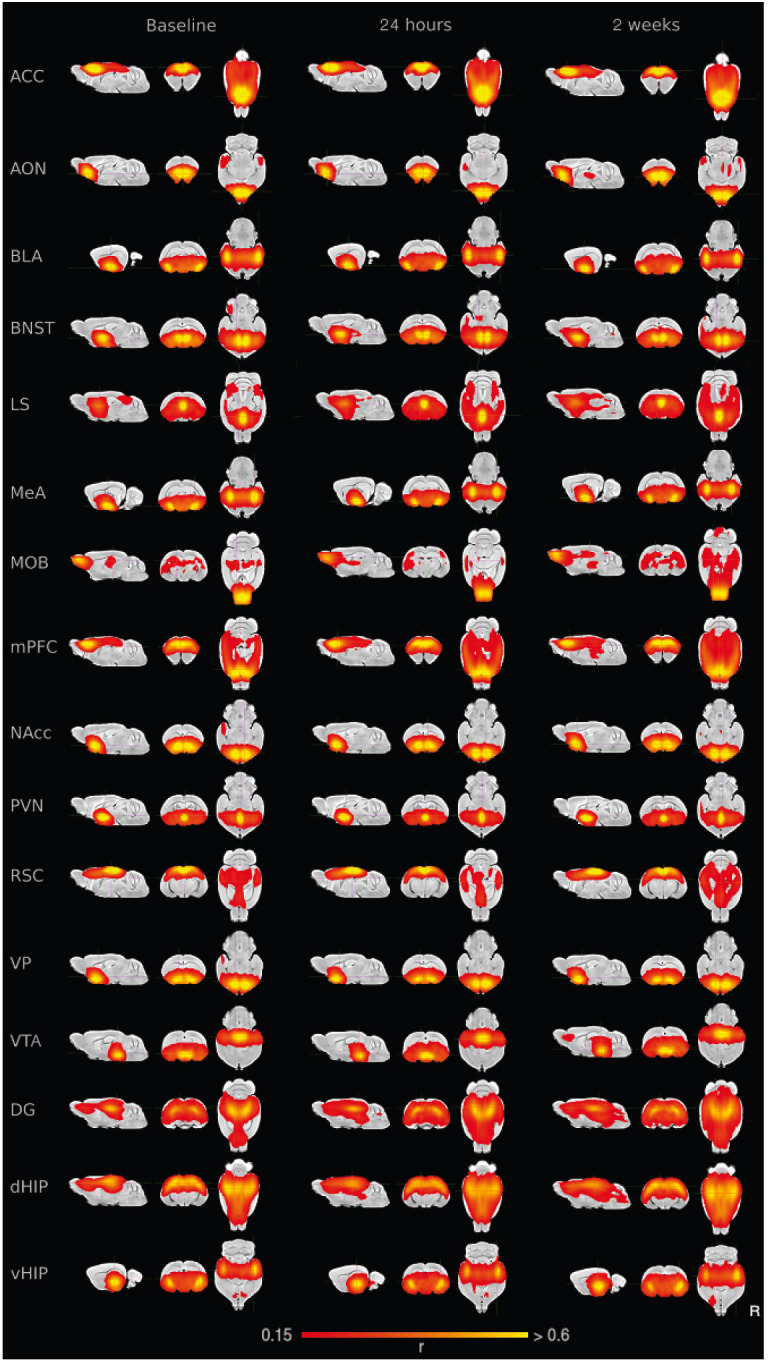
Figure 1—figure supplement 5. Vole temperature during acquisition, discarded images and signal-to-noise ratio.