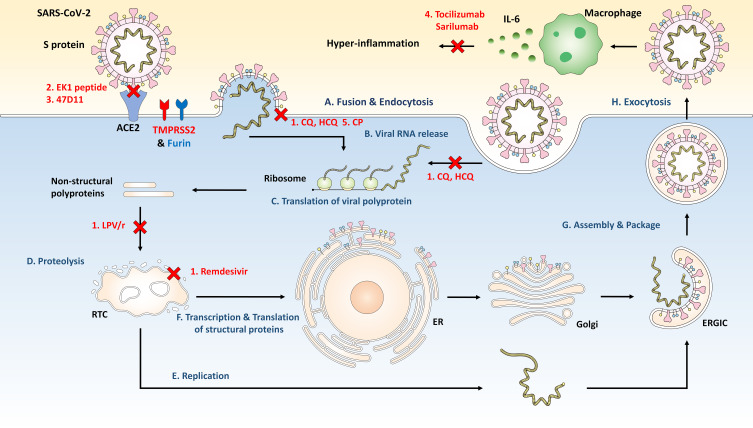
Figure 3.
The SARS-CoV-2 life cycle and potential targets by antiviral agents as therapeutic strategies. (A) SARS-CoV-2 entry in target cell through endocytosis or interaction of S protein and ACE2. (B) Releasing SARS-CoV-2 genomic RNA. (C), (D) Viral polyproteins are translated and cleaved to form a replication transcription complex (RTC). (E) Genomic and subgenomic RNA replication. (F) Subgenomic RNAs produced through the transcription are translated into viral structural proteins inserted in endoplasmic reticulum (ER). (G) The viral nucleocapsid, assembled viral genomic RNA and structural proteins, bud into the lumen of the ER-Golgi intermediate cavity (ERGIC). (H) Exocytosis of SARS-CoV-2. 1. Antiviral drugs; chloroquine (CQ), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r), and remdesivir. 2. S protein and ACE2 interaction inhibitors; EK1 peptide. 3. Neutralizing antibodies; 47D11. 4. Immunotherapy (Anti-interleukin (IL)-6 Drugs); tocilizumab and sarilumab. 5. Convalescent plasma therapy; Convalescent plasma (CP).