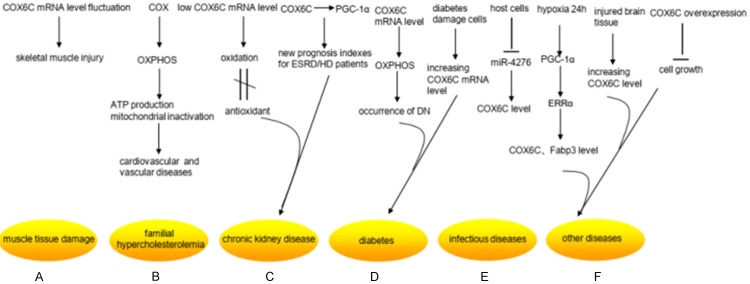
Figure 3.
Research status of COX6C differential expression in non-neoplastic diseases. A. COX6C mRNA was much higher than that of the control group within 6 hours after contusion, but it was going down dramatically at 6-36 hours after injury in the rat muscle injury model. B. COX can regulate oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in eukaryotic enzymes, which can lead to reduced ATP production and mitochondrial inactivation. They contribute to the progression of vascular diseases. C. The expression level of the COX6C mRNA appeared lower in chronic kidney disease (CKD), which revealed the mechanism caused by the imbalance between oxidation and antioxidant defense. COX6C and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1α), an upstream gene of COX6C, can be considered as new prognosis evaluation indexes for end-stage renal disease (ESRD)/HD patients. D. The expression level of COX6C mRNA was remarkably up-regulated in glomerular cells of patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN), manifesting a potential mechanism for the occurrence of DN. The expression of COX6C could increase in diabetes damage cells in the low-intensity laser irradiation. E. Host cells can up-regulate the expression of COX6C by silencing miR-4276 in the early stage of infection with the influenza virus when they first exposed to the influenza virus. F. PGC-1α expression increased in cardiomyocytes after 24 hours under hypoxia condition, which led to an increase in estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), its downstream gene, consequently increased the mRNA expression of COX6C and Fabp3, which was two target genes of ERRα. Moreover, the level mRNA of COX6C was also differentially expressed in the damaged skin cells. And the overexpression of COX6C inhibited cell growth.