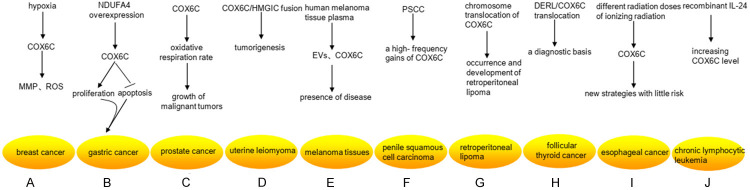
Figure 4.
Research status of COX6C differential expression in cancers. A. Under the hypoxic conditions, the higher level of COX6C promoted the stability of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in MCF-7/MX. B. Overexpression of NDUFA4 remarkably upregulated the expression levels of COX6C, and then promoted the proliferation and decreased the apoptosis of gastric cancer cells. C. The high level of COX6C was necessary for providing a strong oxidative respiration rate to the growth of malignant tumors. D. The COX6C gene was the fused spouse of HMGIC, which was one of the key regulators in tumorigenesis of uterine leiomyoma. E. Mitochondrial protein-enriched extracellular vesicles (EVs) and COX6C could be detected in human melanoma tissue plasma, which reflect the presence of disease. F. COX6C had a high-frequency gains in five penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) cell lines. G. COX6C translocated in ETO8q chromosome breakpoint (8q22) and COX6C (8q22-q23) in retroperitoneal lipoma tissue cells, which was closely related to the occurrence and development of retroperitoneal lipoma. H. DERL/COX6C translocation may provide a diagnostic basis for follicular thyroid cancer. I. The expression of COX6C was significantly up-regulated at the early stage of different radiation doses of ionizing radiation, which may establish new strategies of alternative adjuvant therapy with little risk. J. Recombinant IL-24 stimulated the expression of COX6C after 36 hours, whereas the transcription of COX6C involved in DNA replication and metabolism was hampered within 6 hours.