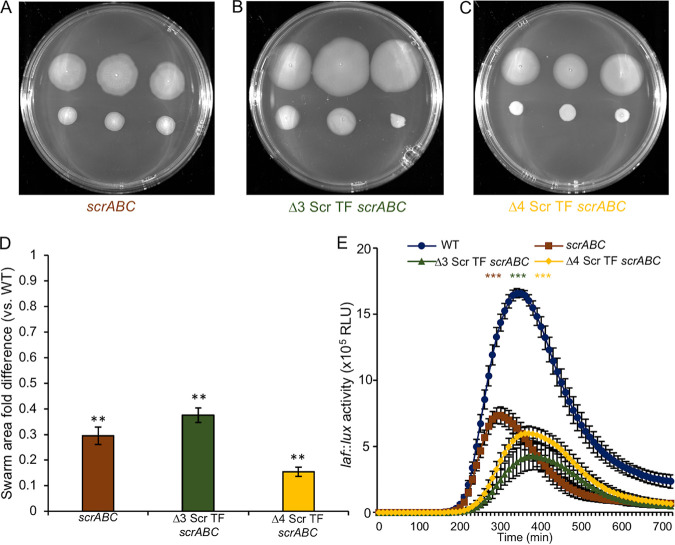
FIG 2.
Deleting three (scrO, cpsQ, and cpsS) or four (scrO, cpsQ, cpsS, and scrP) of the c-di-GMP binding Scr transcription factors (TFs) fails to restore swarming motility when the c-di-GMP level is elevated. (A to C) Three single colonies of the WT (LM4476) (top) and three colonies, as indicated, of the scrABC (LM11253) (A), Δ3 Scr TF scrABC (LM11427) (B), or Δ4 Scr TF scrABC (LM11430) (C) strain (bottom). (D) Quantification of ratios of swarm areas of the mutants to the WT in swarm assays performed as described above for panels A to C. The average swarm area ratio of the mutant versus the wild type was calculated for each plate, i.e., three swarming colonies of each mutant and the wild type grown on the same plate. Bars represent the averages of the ratios from at least three plates; error bars denote the standard errors. Pairwise comparisons were performed using Student’s t test (**, P < 0.01). (E) Lateral flagellar (laf::lux) gene expression during surface growth of the WT (LM1017 parental strain with flgE::lux), scrABC (LM11524), Δ3 Scr TF scrABC (LM11285), and Δ4 Scr TF scrABC (LM11525) strains. For each mutant, pairwise comparisons of maximum relative luminescence units (RLU) were performed against the WT, and statistical significance is color coordinated (***, P < 0.001).