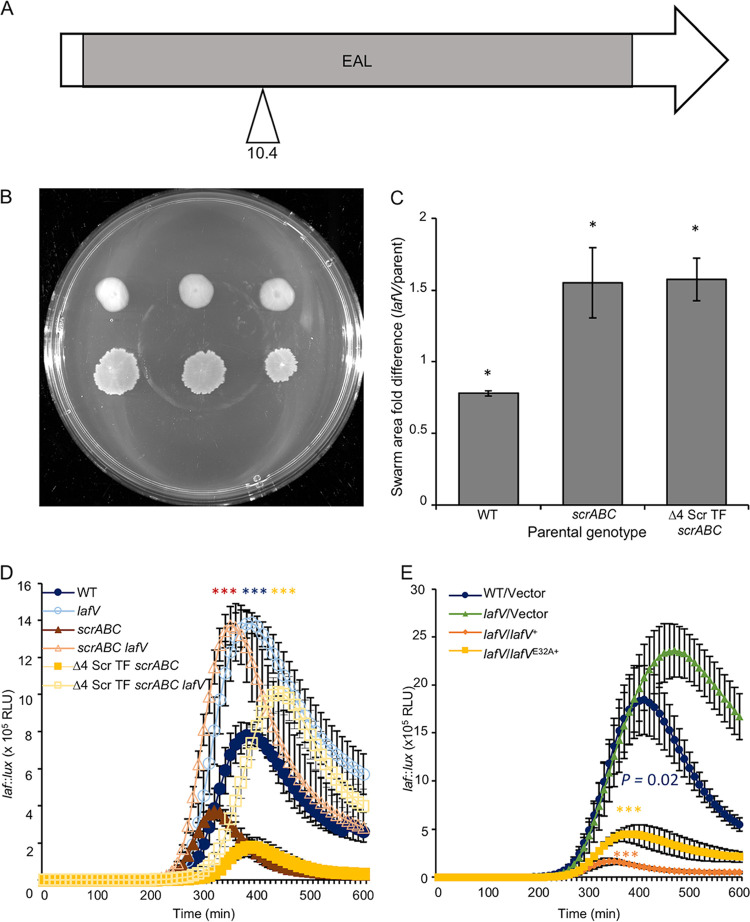
FIG 5.
LafV is an EAL domain-containing protein that negatively affects swarming. (A) Predicted domain organization of LafV (31 kDa). The gray box indicates the putative EAL domain. (B) Three swarming colonies for each strain, Δ4 Scr TF scrABC (LM11985) (top) and Δ4 Scr TF scrABC lafV (LM12003) (bottom). (C) Quantification of the ratios of swarm areas of the indicated strain pairings (x axis) in swarm assays performed as described above for panel B in addition to the lafV (LM12001)/WT (LM4476) and scrABC lafV (LM12002)/scrABC (LM11984) strains. (D and E) Lateral flagellar (laf::lux) gene expression during surface growth. (D) WT (LM1017 with flgE::lux), lafV (LM11998), scrABC (LM11524), scrABC lafV (LM11999), Δ4 Scr TF scrABC (LM11525), and Δ4 Scr TF scrABC lafV (LM12000) strains (n = 6). Pairwise comparisons of maximum RLU between lafV mutants and their isogenic lafV+ parent (e.g., LM1017 versus LM11998) were performed using Student’s t test (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (E) WT/V (LM12049), lafV/V (LM12050), lafV/lafV+ (LM12051), and lafV/lafVE32A (LM12052) strains. Strains were grown with 100 μM IPTG (n = 6). Pairwise comparisons between maximum RLU were performed against LM12050 using Student’s t test (***, P < 0.001).