FIG 3.
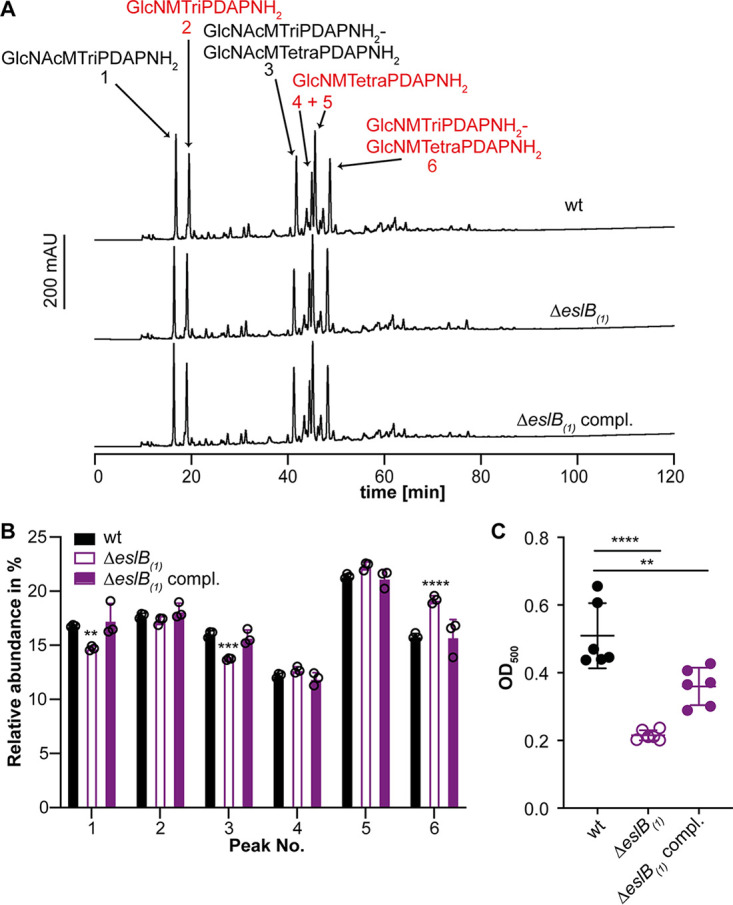
Deletion of eslB leads to changes in the peptidoglycan structure. (A) HPLC analysis of muropeptides derived from mutanolysin-digested peptidoglycan isolated from strains 10403S (wt), 10403SΔeslB1, and 10403SΔeslB1 compl. The muropeptide spectrum of the wild-type strain 10403S was published previously (43). Major muropeptide peaks are labeled and numbered 1 to 6 according to previously published HPLC spectra (18, 44), with labels in red corresponding to muropeptides with N-deacetylated GlcNAc residues and peaks 1 and 2 corresponding to monomeric and 4 to 6 to dimeric (cross-linked) muropeptide fragments. Muropeptide abbreviations: GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; GlcN, glucosamine; M, N-acetylmuramic acid; TriPDAPNH2, l-alanyl-γ-d-glutamyl-amidated meso-diaminopimelic acid; TetraPDAPNH2, l-alanyl-γ-d-glutamyl-amidated meso-diaminopimelyl-d-alanine. (B) Quantification of the relative abundance of muropeptide peaks 1 to 6 for peptidoglycan isolated from strains 10403S (wt), 10403SΔeslB1, and 10403SΔeslB1 compl. For quantification, the sum of the peak areas was set to 100% and the area of individual peaks was determined. Average values and standard deviations were calculated from three independent peptidoglycan extractions and plotted. For statistical analysis, a two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test was used (**, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001). (C) The degree of O-acetylation of purified peptidoglycan of strains 10403S (wt), 10403SΔeslB1, and 10403SΔeslB1 compl. was determined by a colorimetric assay as described in Materials and Methods. Average values and standard deviations were calculated from three independent peptidoglycan extractions and two technical repeats and plotted. For statistical analysis, a two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test was used (**, P ≤ 0.01; ****, P ≤ 0.0001).
