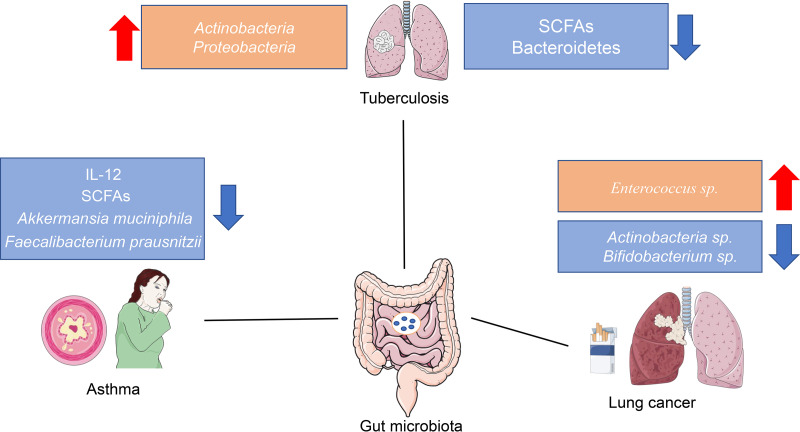
FIG 2.
The dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in some lung diseases. An increasing number of studies have suggested that the composition of the gut microbiota and its products change in different lung diseases. For example, obvious decreases in Akkermansia muciniphila, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, and SCFA levels are observed in patients with asthma. Some studies found that the abundances of Actinobacteria spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. decreased in patients with lung cancer. However, the underlying mechanism and relationship between the gut microbiota and lung diseases are still unclear, and additional animal studies and clinical trials are required to understand the complex interactions of the gut microbiota and lung diseases.