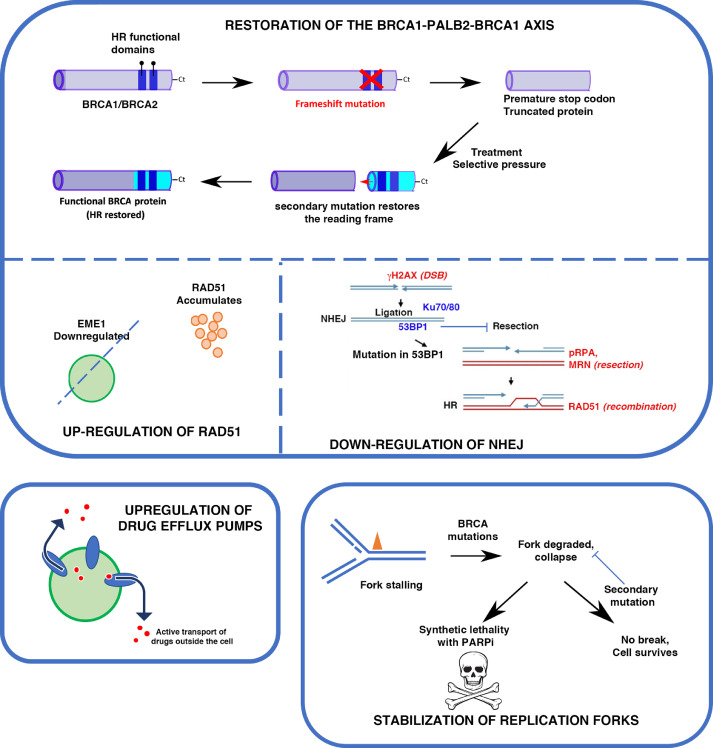
Fig. 3.
Major mechanisms of resistance to PARPi. Top panel: Restoration of HR by acquisition of secondary mutations in HR genes, or in NHEJ genes. Bottom left panel: drug efflux pumps can decrease intracellular concentration of drugs such as PARPi. Bottom right: Stabilization of forks allow rescue even in the absence of other cellular components, and reverse the synthetic lethality, thus rendering cells resistant to PARPinhibition.