Figure 3.
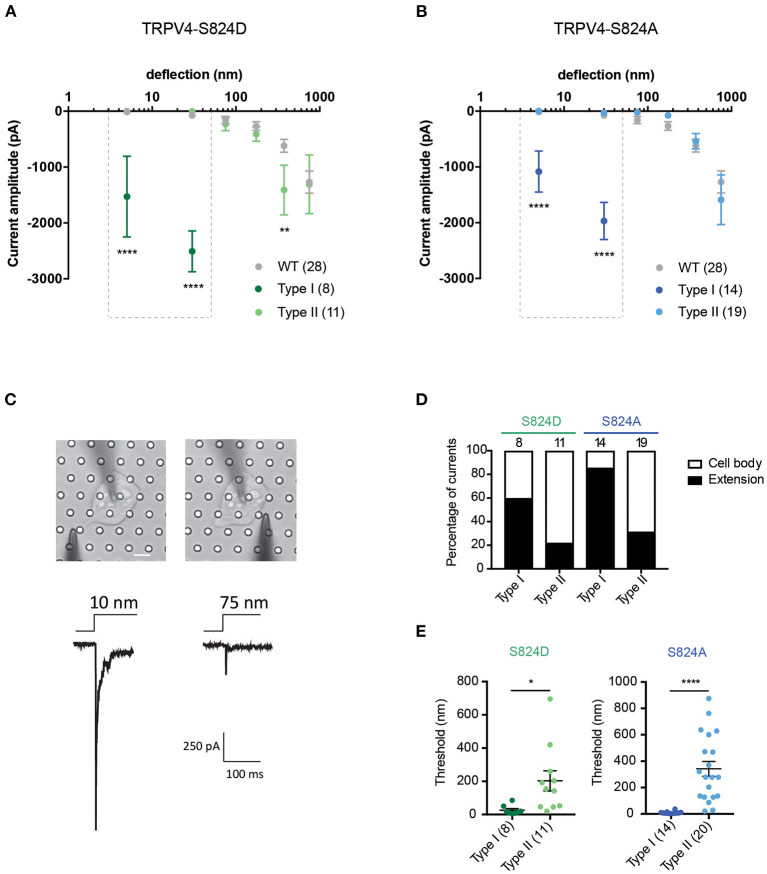
Phosphorylation site, S824 regulates TRPV4-mediated currents in response to pillar deflection. Stimulus-response plots for (A) TRPV4-S824D and (B) TRPV4-S824A in comparison to WT cultured on R3 substrate. Currents from TRPV4-S824D and TRPV4-S824A expressing cells were categorized into two types based on their sensitivity to deflection at a given pilus: Type I with high sensitivity and Type II with lower sensitivity. Ordinary two-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparisons was used to analyze the plots. The first two bins (1–10 and 10–50 nm) were analyzed separately for Type I vs. Type II and Type I vs. WT as indicated in the dashed boxes (****p < 0.0001, Type I = 8 stimulation points vs. Type II = 11; WT = 28). Type II was compared to WT for all six bins (1–1,000 nm) and **p = 0.0083 for TRPV4-S824D for bin 250–500 nm (Type II = 11 stimulation points and WT = 28). (C) Bright-field image of a single HEK-293T cell expressing TRPV4-S824D and the corresponding current traces. Ten nanometer deflection of the pili subjacent to the cell extension resulted in current amplitude of 1,315 pA, while 75 nm deflection applied to the cell body of the same cell generated 265 nA current. (D) Percentage of type I and type II currents in TRPV4-S824D and TRPV4-S824A cells based on the site of deflection. The majority of Type I currents were observed upon deflection of the cell extensions rather than cell body. (E) Activation threshold for type I and type II currents in TRPV4-S824D and TRPV4-S824A cells was measured by averaging the smallest deflections generating currents. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m, number in brackets indicates number of stimulation points (*p < 0.05). Full details on cell numbers outlined in Supplementary Table 1.